Summary
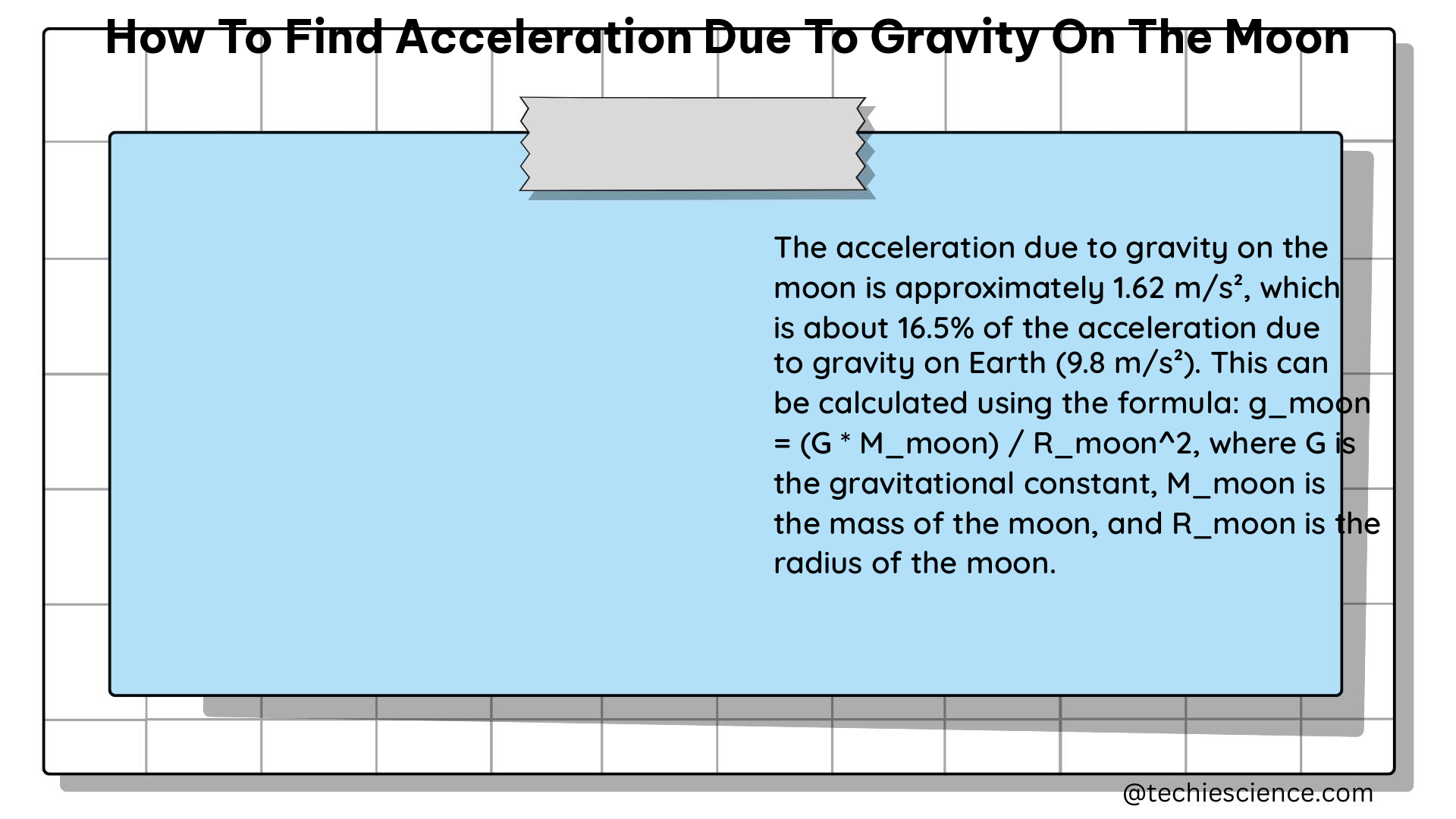
The acceleration due to gravity on the moon, denoted as “g,” is approximately 1.625 m/s². This value is about one-sixth of the acceleration due to gravity on Earth, which is 9.81 m/s². To calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the moon, we can use the formula: g = (G * M) / R², where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the moon, and R is the radius of the moon.
Understanding the Concept of Gravity on the Moon
Gravity is a fundamental force in the universe that governs the motion of celestial bodies and the behavior of objects on Earth. The acceleration due to gravity, often represented as “g,” is a measure of the rate at which an object’s velocity changes due to the force of gravity.
On Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.81 m/s², which means that an object near the Earth’s surface will accelerate downward at a rate of 9.81 meters per second squared. This value is relatively constant across the surface of the Earth, with minor variations due to factors such as latitude and altitude.
However, the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is significantly lower than on Earth. This is because the moon has a much smaller mass and a larger radius compared to the Earth, which affects the strength of the gravitational field.
Calculating the Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Moon
To calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the moon, we can use the formula:
g = (G * M) / R²
Where:
– g is the acceleration due to gravity on the moon (in m/s²)
– G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10^-11 N m²/kg²)
– M is the mass of the moon (7.342 × 10^22 kg)
– R is the radius of the moon (1,737,000 m)
Plugging in the values, we get:
g = (6.674 × 10^-11 N m²/kg²) × (7.342 × 10^22 kg) / (1,737,000 m)²
g ≈ 1.625 m/s²
Therefore, the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s².
Factors Affecting the Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Moon
The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is influenced by several factors, including:
-
Mass of the Moon: The mass of the moon is a crucial factor in determining the acceleration due to gravity. The moon has a much smaller mass compared to the Earth, which results in a weaker gravitational field and a lower acceleration due to gravity.
-
Radius of the Moon: The radius of the moon is another important factor. The larger the radius, the weaker the gravitational field, and the lower the acceleration due to gravity. The moon has a radius of approximately 1,737,000 meters, which is significantly larger than the Earth’s radius of approximately 6,371,000 meters.
-
Gravitational Constant: The gravitational constant, denoted as “G,” is a fundamental physical constant that represents the strength of the gravitational force between two objects. The value of the gravitational constant is approximately 6.674 × 10^-11 N m²/kg².
-
Location on the Moon: The acceleration due to gravity on the moon can vary slightly depending on the location on the lunar surface. This is due to factors such as the uneven distribution of mass within the moon and the presence of surface features like mountains and craters.
Comparison of Gravity on the Moon and Earth
The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is significantly lower than on Earth. Here’s a comparison:
- Acceleration due to gravity on Earth: 9.81 m/s²
- Acceleration due to gravity on the moon: 1.625 m/s²
This means that the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is approximately one-sixth of the acceleration due to gravity on Earth. This has several implications:
-
Reduced Gravitational Force: Objects on the moon experience a much weaker gravitational force compared to objects on Earth. This is why astronauts can jump higher and move more easily on the lunar surface.
-
Reduced Tidal Forces: The lower acceleration due to gravity on the moon results in weaker tidal forces, which are the forces that cause the rise and fall of the tides on Earth.
-
Reduced Surface Gravity: The lower acceleration due to gravity on the moon means that objects and people on the lunar surface experience a reduced surface gravity, which can have physiological effects on the human body, such as muscle atrophy and bone loss.
Practical Applications and Implications
The understanding of the acceleration due to gravity on the moon has several practical applications and implications:
-
Space Exploration: The knowledge of the moon’s gravity is crucial for planning and executing successful space missions. It helps engineers design spacecraft, landers, and rovers that can operate effectively on the lunar surface.
-
Lunar Experiments and Observations: The lower gravity on the moon allows for unique experiments and observations that are not possible on Earth. For example, the reduced gravity can be used to study the behavior of fluids, the motion of objects, and the effects of gravity on living organisms.
-
Lunar Resource Utilization: The lower gravity on the moon may facilitate the extraction and processing of lunar resources, such as minerals and water ice, which could be used to support future lunar settlements and space exploration.
-
Lunar Habitat Design: The reduced gravity on the moon has implications for the design of lunar habitats and the development of technologies to support human life on the lunar surface, such as life support systems and transportation.
-
Lunar Navigation and Dynamics: Understanding the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is essential for accurately predicting the motion and trajectories of spacecraft and other objects in the lunar environment.
Conclusion
In summary, the acceleration due to gravity on the moon is approximately 1.625 m/s², which is about one-sixth of the acceleration due to gravity on Earth. This value is calculated using the formula g = (G * M) / R², where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the moon, and R is the radius of the moon. The lower acceleration due to gravity on the moon has significant implications for space exploration, lunar experiments, resource utilization, habitat design, and lunar navigation and dynamics.
References
- Byjus – Value of g on the Moon
- YouTube – Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Moon
- Byjus – Find the Value of Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Surface of the Moon
- Vaia – Calculate the Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Moon
- CK12 – How Do You Calculate the Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Moon?

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.