Planck’s constant, denoted as “h,” is a fundamental physical constant that plays a crucial role in quantum mechanics. It represents the smallest possible change in any physical action or energy. This constant is essential for calculating the energy of photons, which are the fundamental particles of light. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of how to calculate energy using Planck’s constant.
Understanding the Planck-Einstein Relation
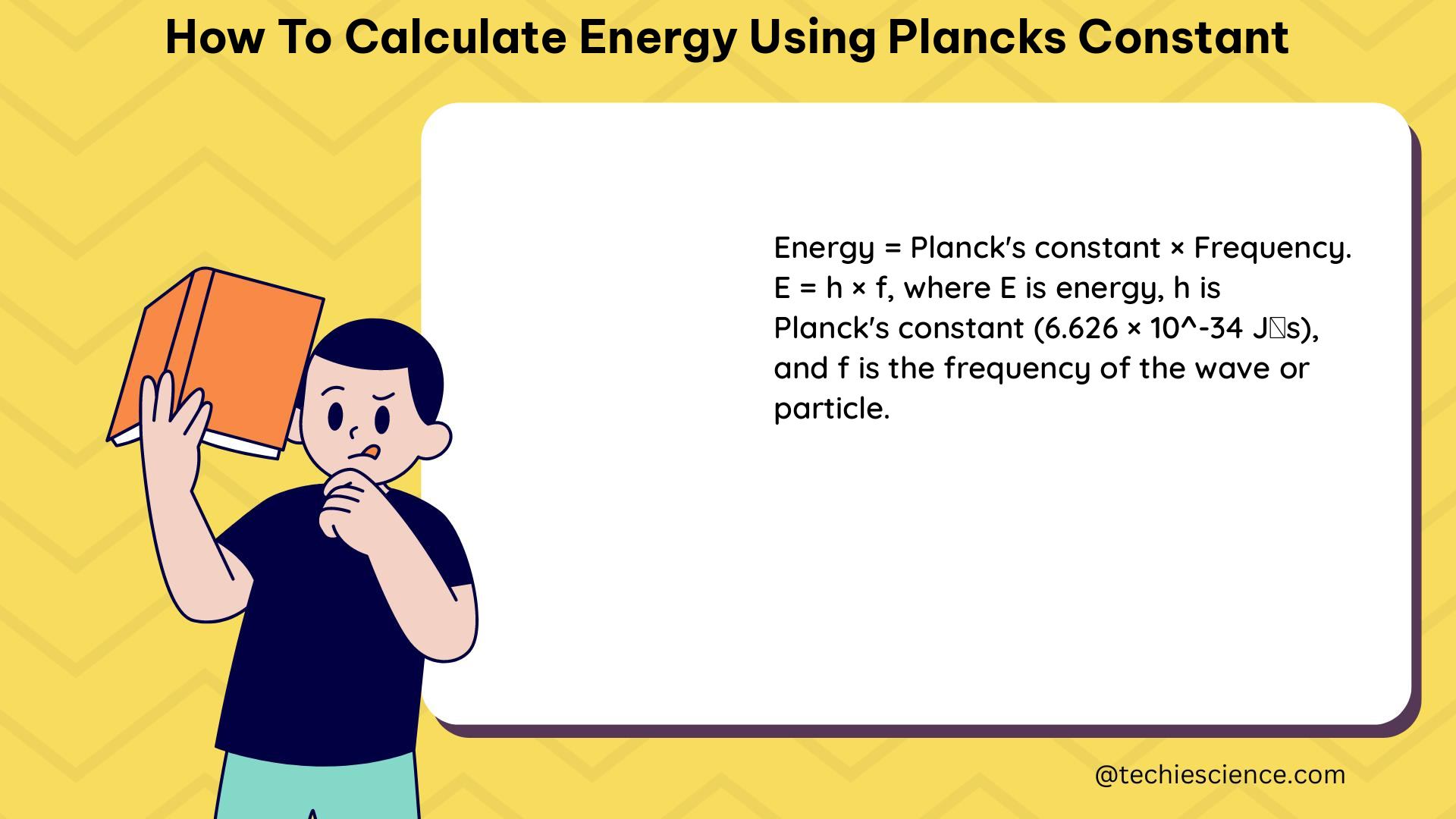
The Planck-Einstein relation is the equation that connects the energy of a photon to its frequency. This equation is expressed as:
E = hf
Where:
– E is the energy of the photon
– h is Planck’s constant (6.62607015 × 10^-34 J⋅s)
– f is the frequency of the photon
This equation is a fundamental principle of quantum mechanics and is used to describe the relationship between the energy and frequency of photons.
Measuring the Frequency of Light
To use the Planck-Einstein relation, you need to know the frequency of the light you are working with. There are several methods to measure the frequency of light, and one of the most common is using a spectrometer.
Using a Spectrometer
A spectrometer is an instrument that measures the wavelength and intensity of light. One example is the Eisco spectroscope (cat no. PH 0100QA), which can be used to measure the dominant frequency of LEDs emitting visible light.
The Eisco spectroscope passes light through a slit with a 500 lines/mm diffraction grating on the viewing end. It has a scale that shows the frequency of the light in nanometers, which can be seen when looking through the viewfinder.
To calculate the wavelength of the spectra, you can use the equation:
y = λL/d
Where:
– y is the distance from the center to the spectral line being measured in meters (m) on the scale
– λ is the wavelength (m)
– L is the distance from the diffraction grating to the slit in meters (0.19 m)
– d is the spacing of the grating
Once you have the wavelength, you can calculate the frequency using the formula:
f = c/λ
Where:
– f is the frequency of the light
– c is the speed of light (3 × 10^8 m/s)
– λ is the wavelength of the light
Calculating the Energy of a Photon
Now that you have the frequency of the light, you can use the Planck-Einstein relation to calculate the energy of a photon.
The equation is:
E = hf
Where:
– E is the energy of the photon
– h is Planck’s constant (6.62607015 × 10^-34 J⋅s)
– f is the frequency of the light
Let’s consider an example:
Suppose you want to calculate the energy of a photon of blue light with a frequency of 6.2 × 10^14 hertz. You can plug the values into the equation as follows:
E = (6.62607015 × 10^-34 J⋅s) × (6.2 × 10^14 Hz)
E = 4.1 × 10^-19 Joules
Therefore, the energy of each photon of blue light is 4.1 × 10^-19 Joules.
Applications of Planck’s Constant
In addition to its use in calculating the energy of photons, Planck’s constant is also used in other areas of quantum physics, such as:
- de Broglie Relationship: Planck’s constant is used in the de Broglie relationship, which describes the wavelength of matter waves.
- Schrödinger’s Wave Equation: Planck’s constant is a key component of Schrödinger’s Wave Equation, which is used to describe the behavior of quantum systems.
- Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: Planck’s constant is used in Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle, which states that the position and momentum of a particle cannot be measured simultaneously with arbitrary precision.
- Defining Measurement Units: Planck’s constant is used to define measurement units in everyday use, such as the kilogram.
Conclusion
Planck’s constant is a fundamental physical constant that is essential for understanding the behavior of photons and other quantum phenomena. By using the Planck-Einstein relation, you can calculate the energy of a photon based on its frequency. This knowledge is crucial for many applications in quantum physics and modern technology.
References
- Planck Constant – Wikipedia
- Planck’s Constant Formula & Application
- The Planck Constant and the Relationship of Frequency to Photon Energy

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.