In the realm of particle physics, understanding the energy involved in particle collisions is crucial for unraveling the fundamental nature of the universe. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of calculating the energy in a particle collision, providing you with a robust understanding of the underlying principles and practical applications.
Kinetic Energy of Particles
The starting point for calculating the energy in a particle collision is the kinetic energy of the individual particles involved. The kinetic energy (KE) of a particle can be calculated using the formula:
KE = 1/2 * m * v^2
Where:
– KE is the kinetic energy of the particle
– m is the mass of the particle
– v is the velocity of the particle
This formula allows us to determine the kinetic energy of each particle based on its mass and velocity.
Center-of-Mass Energy (Ecm)
In the context of particle collisions, the total energy of the collision is often referred to as the center-of-mass energy (Ecm). This energy is the sum of the kinetic energies of the colliding particles, calculated in the center-of-mass frame of reference.
The formula for the center-of-mass energy is:
Ecm = KE1 + KE2
Where:
– KE1 and KE2 are the kinetic energies of the two colliding particles.
By calculating the kinetic energies of the individual particles and then summing them, we can determine the total center-of-mass energy of the collision.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider an example of two particles with masses m1 and m2, and velocities v1 and v2, respectively. The center-of-mass energy of their collision can be calculated as follows:
Ecm = 1/2 * m1 * v1^2 + 1/2 * m2 * v2^2
This formula allows us to determine the center-of-mass energy based on the masses and velocities of the colliding particles.
Practical Considerations
In practice, the velocities of the colliding particles are often not known directly. Instead, the energies and momenta of the particles are measured, and the velocities are calculated from these measurements.
Once the velocities are known, the kinetic energies can be calculated, and the center-of-mass energy can be determined as the sum of the kinetic energies.
Mass-Energy Equivalence
In particle physics, the center-of-mass energy is often expressed in terms of the mass-energy equivalence, using the formula E = mc^2. This allows for the calculation of the total energy of a particle, including its rest mass energy.
For example, if two particles each have a rest mass energy of 1 GeV, and they are moving towards each other with a center-of-mass energy of 2 GeV, the total energy of each particle in the center-of-mass frame can be calculated as:
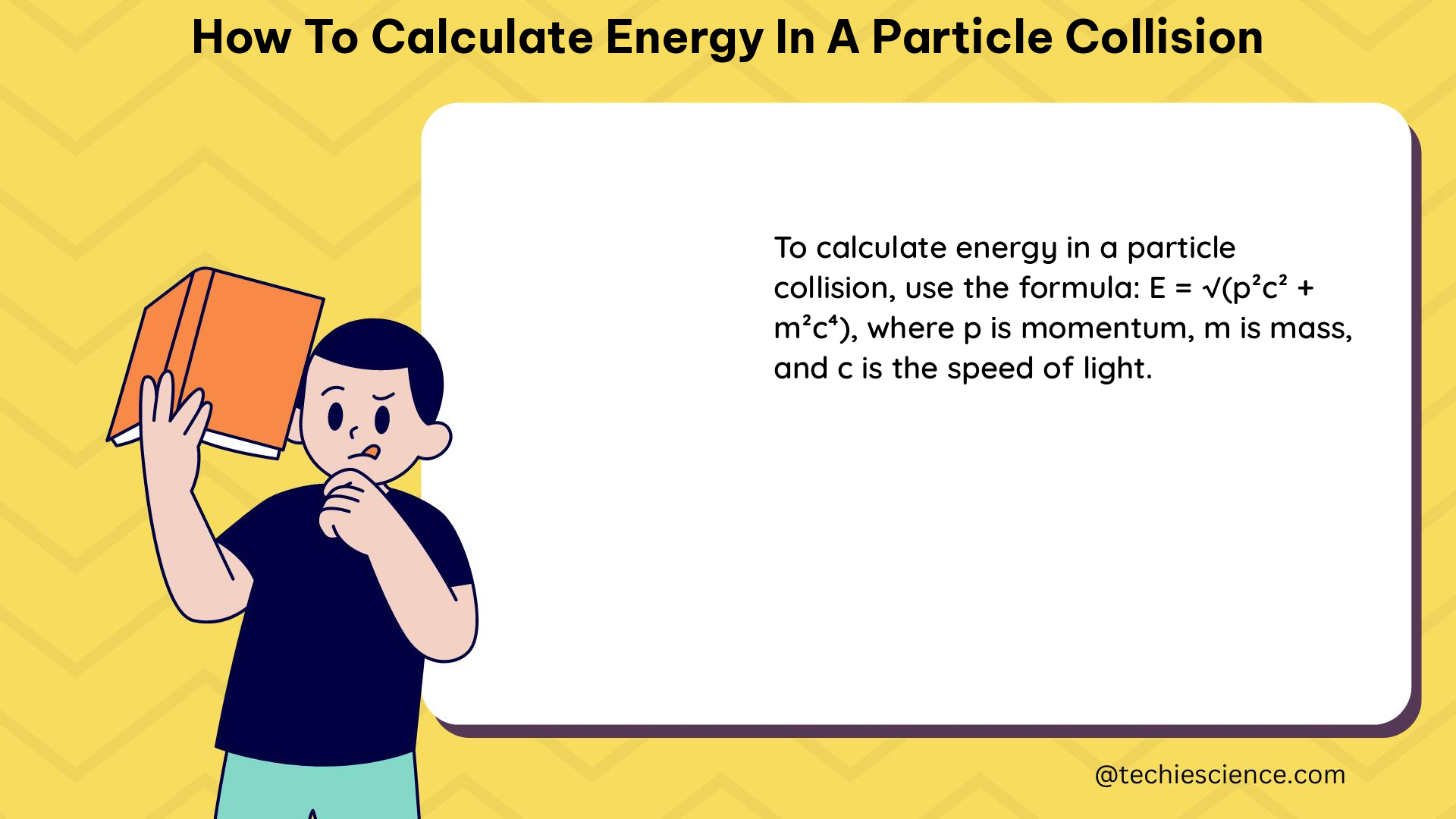
E = sqrt(m^2c^4 + p^2c^2)
Where:
– m is the rest mass energy of the particle
– p is the momentum of the particle
– c is the speed of light
By solving for the momentum (p) and then calculating the velocities, we can determine the kinetic energies and the center-of-mass energy of the collision.
Numerical Example
Let’s consider a specific numerical example to illustrate the calculations:
Suppose two particles, each with a rest mass energy of 1 GeV, are moving towards each other with a center-of-mass energy of 2 GeV.
-
Calculating the momentum (p):
p = sqrt(E^2 – m^2c^4) / c
p1 = sqrt((1 GeV)^2 + (1 GeV)^2) / c = 1.41 GeV/c
p2 = -1.41 GeV/c -
Calculating the velocities (v):
v = p / (m * c)
v1 = 1.41 GeV/(1 GeV * c) = 1
v2 = -1.41 GeV/(-1 GeV * c) = 1 -
Calculating the kinetic energies (KE):
KE = 1/2 * m * v^2
KE1 = 1/2 * 1 GeV * (1 c)^2 = 0.5 GeV
KE2 = 0.5 GeV -
Calculating the center-of-mass energy (Ecm):
Ecm = KE1 + KE2 = 1 GeV + 0.5 GeV = 1.5 GeV
This example demonstrates the step-by-step process of calculating the energy in a particle collision, considering the mass-energy equivalence and the center-of-mass frame.
Conclusion
Calculating the energy in a particle collision is a fundamental aspect of particle physics, enabling researchers to unravel the mysteries of the universe. By understanding the principles of kinetic energy, center-of-mass energy, and mass-energy equivalence, you can effectively determine the energy involved in various particle collision scenarios. This comprehensive guide has provided you with the necessary tools and knowledge to tackle these calculations with confidence.
References
- Particle Collision Energy Calculations
- Electromagnetic Interactions: Particle Collisions
- How’s the Energy of Particle Collisions Calculated?

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.