HI is the formula of hydrogen Iodide, which is a strong acid. Magnesium carbonate occurs in the form of mineral magnesite. Let us predict the reaction of HI+MgCO3 in this article.
Hydrogen iodide is a colorless gas with a molar mass of 127.904g/mol. Hydrogen iodide is a gas, whereas hydroiodic acid is an aqueous solution of the gas. Magnesium carbonate is colorless to white solid. It is the source of the magnesium element. MgCO3 extracted from the ore Dolomite.
In this article, we will go through various facts related to the HI+MgCO3 reaction.
What is the product of HI and MgCO3
The product of the HI+MgCO3 reaction is MgI2, CO2 and H2O. Magnesium iodide form is a salt of strong acid.
MgCO3+2HI ⟶ MgI2 +CO2 +H2O.
What type of reaction is HI + MgCO3
HI+MgCO3 is an acid-base reaction. In HI+MgCO3, HI is a strong acid, whereas MgCO3 is a salt of a weak acid and is basic in nature.
MgCO3 (base) +2HI (acid) ⟶ MgI2 (salt of strong acid) +CO2 +H2O.
How to balance HI + MgCO3
To balance an equation following steps are followed.
- First, we have to find out the number of atoms on the reactant site and a number of atoms on the product site.
- In the MgCO3+HI ⟶ MgI2 +CO2 +H2O reaction on the reactant side, one hydrogen atom, one iodine atom, one magnesium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms are present.
- On the other hand, on the product side, two hydrogen atoms, two iodine atoms, one magnesium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms are present.
- This can be tabulated below.
| Atom | Number of Reactants | Number of product |
|---|---|---|
| H | 1 | 2 |
| I | 1 | 2 |
| Mg | 1 | 1 |
| C | 1 | 1 |
| O | 3 | 3 |
- As given in above table we can understand that both the reactant and product sides have unequal distribution of atoms. So we have to balance this using the Algebraic method given below.
| Atom | Number of Reactant | Number of product |
|---|---|---|
| H | 2 | 2 |
| I | 2 | 2 |
| Mg | 1 | 1 |
| C | 1 | 1 |
| O | 3 | 3 |
- Thus balanced reaction can be written as
- 2HI+MgCO3⟶ MgI2+CO2+H2O.
HI + MgCO3 net ionic equation
Net ionic equation of HI+MgCO3 is 2H+ (g) + CO32-(aq) ⟶ H2O (l) +CO2 (g).
- We have to write the complete ionic equation.
- 2H+ (g) +2I– (g) +Mg2+ (aq) +CO32- (aq) ⟶Mg2+ (aq) +2I– (g) + H2O (l) +CO2 (g).
- In this step we have to cancel the element with the same ions on both side of reaction.
- 2H+ (g) +2I– (g) +Mg2+ (aq) +CO32- (aq) ⟶Mg2+ (aq) +2I– (g) + H2O(l) +CO2 (g).
- Thus 2I– and Mg2+ will be cancelled as present on both side of reaction. After canceling these ions, the remaining ion will form a net ionic equation.
- 2H+ (g) +CO32- (aq) ⟶H2O (l) +CO2 (g).
HI + MgCO3 conjugate pairs
HI + MgCO3 reaction has following Conjugate acid bases differ from each other with a difference of one proton between them.
- The conjugate base of HI ⟶ I-
- The conjugate base of MgCO3 ⟶ CO3-
- The conjugate base of H2O ⟶ OH-
HI and MgCO3 intermolecular forces
HI + MgCO3 reaction has following intermolecular forces,
- In HI, dipole-dipole interaction and London dispersion forces are present.
- In MgCO3, there are Mg2+ and CO23- ions present. Mg is metal, and CO3 is non-metal, together forming an ionic compound and showing the electrostatic force of attraction.
HI + MgCO3 reaction enthalpy
The reaction enthalpy of HI + MgCO3 is +0.46 kJ mol – 1. This can be calculated given below.
- Step 1 finds out the enthalpy of the formation of is compound on the reactant side as well as on the product side, which is tabulated as.
| Compound | Enthaply of formation (KJ mol-1) |
|---|---|
| HI | 26 |
| MgCO3 | -1095.8 |
| MgI2 | -364 |
| CO2 | -393.51 |
| H2O | -285.83 |
- The enthalpy of the reaction is calculated below.
- Enthalpy of reaction = some of the enthalpy on the product side – some of the enthalpy on the reactant side = (-364) + (-393.51) + (-285.83)-(2*26) + (-1095.8)= +0.46 KJ mol-1.
Is HI + MgCO3 a buffer solution
HI+MgCO3 is not a buffer solution as HI is a strong acid. Buffer is a solution from by solution of weak acid and salt of that weak acid or a solution of a weak base and salt of that weak base. This condition is not applied here.
Is HI + MgCO3 a complete reaction
HI + MgCO3 is a complete reaction as a complete mole of reactant consumed by the product at equilibrium.
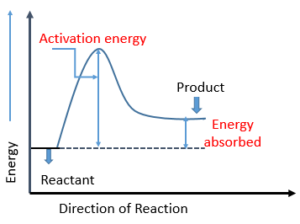
Is HI + MgCO3 an exothermic or endothermic reaction
HI + MgCO3 is an endothermic reaction as reaction enthalpy has a positive value at +0.46KJ mol-1. Thus heat is absorbed during HI + MgCO3 reaction. Thus reactant is more stable than a product.
Is HI + MgCO3 a redox reaction
HI + MgCO3 is not a redox reaction, as there is no transfer of electrons. The oxidation state of the element on the reactant side and product side is same. Thus, no change in the oxidation state was found.
Is HI + MgCO3 a precipitation reaction
HI + MGCO3 is not a precipitation reaction as no precipitate formed during HI + MgCO3 reaction. MgI2 formed on a product is highly water soluble.
Is HI + MgCO3 reversible or irreversible reaction
HI + MgCO3 is an irreversible reaction as CO2 formed on the product side is a gas molecule, so there is no chance of reversibility of the reaction.
Is HI + MgCO3 displacement reaction
HI + MgCO3 is a single displacement reaction. HI +MgCO3 reaction gives different compounds which result of interchange of anions and cations of reactant side.
Conclusion
Hydrogen iodide is used as a reducing agent. In organic and inorganic synthesis, it has a main role as a source of iodine. Magnesium carbonate is used as paint additives as well as food additives. MgCO3 is also used in the cosmetic industry. Pure-grade magnesium oxide can be formed from it.

Hello everyone I am Arti D. Gokhale. My master’s with a specialization in Organic Chemistry and I graduated with Chemistry, Biology, and Zoology. I have 3 years of work experience in water analysis at the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute Nagpur.