Hydrochloric acid and Silver Chloride are both inorganic compounds containing chlorine. Let us see interesting properties of their reaction.
HCl is a strong Bronsted acid that can be isolated in both gaseous and aqueous form. Silver Chloride, a white solid, shows more of an ionic character due to the lesser polarising ability of the larger Ag+ ion. While HCl can be prepared by dissolving hydrogen chloride in aqueous solution.
Since both compounds have a common element, let us dive into how their reaction occurs in this article.
What is the product of HCl and AgCl?
HCl and AgCl are combined in aqueous medium due to better yield. The purported reaction scheme is:
- AgCl + HCl + H2O = Ag+ + H3O+ + 2Cl–
What type of reaction is HCl and AgCl?
An ionic reaction is generally observed on reacting AgCl in HCl.
How to balance HCl and AgCl?
Following are the steps to equate the above reaction scheme:
- AgCl = Ag+ + Cl–
- HCl + H2O = H3O+ + Cl–
- AgCl + HCl + H2O = Ag+ + H3O+ + 2Cl–
HCl + AgCl Titration
The titration of AgCl with HCl will yield no significant results due to no noticeable colour change in such reactions. However, we can use standardised HCl to titrate AgCl if AgNO3 is added since the reaction will be accompanied by a colour change. Moreover, AgCl has very low solubility in water.
- AgCl = Ag+ + Cl–
- Ksp = [Ag+] [Cl–]
| Silver Halide | Ksp in water |
|---|---|
| Silver Chloride(AgCl) | 2 x 10-10 |
| Silver Bromide(AgBr) | 5 x 10-13 |
| Silver Iodide(AgI) | 8 x 10-17 |
HCl + AgCl Net Ionic Equation
The net ionic equation stands as:
- AgCl + HCl + H2O = Ag+ + H3O+ + 2Cl–
HCl + AgCl Conjugate Pairs
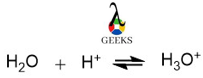
Conjugate acid-base pairs refer those pair of compounds where the chemical difference between them is just one proton. For instance,
- H2O + H+ = H3O+ , here upon protonation of water, hydronium ion is formed.
- Conjugate acid of H2O= H3O+
- Conjugate base of AgCl= Cl–
HCl + AgCl Intermolecular Forces
Both AgCl and HCl show ionic intermolecular interactions in aqueous medium. HCl shows low dipole-dipole interactions while the electrostatic interactions in AgCl are less polarized in nature.
HCl + AgCl Reaction Enthalpy
Proper data of the reaction enthalpy has not been reported as the reaction of HCl and AgCl may dissipate energy and becomes feasible.
Is HCl + AgCl a Buffer Solution?
HCl + AgCl combination will not yield a strong buffer solution as the acid should be weak so that adding acid does not alter the pH considerably. While hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, silver chloride is a weak salt of a strong acid.
Is HCl + AgCl a Complete Reaction?
The HCl + AgCl reaction is complete as an equilibrium can be reached when the common ion effect occurs.
- AgCl + HCl + H2O = Ag+ + H3O+ + 2Cl–
Is HCl + AgCl an Exothermic Reaction?
The resultant HCl + AgCl reaction can be slightly exothermic as the addition of chloride ions from hydrochloric acid develops a backward equilibrium to produce more reactants.
Is HCl + AgCl a Redox Reaction?
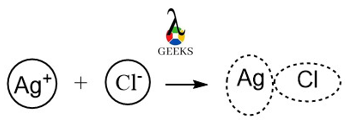
The HCl + AgCl reaction system occurs with change in ions and can be termed as redox reaction .In the reaction, Ag+ ion is formed from the compound AgCl. Ionisation might occur due to transfer of electron, as shown below:
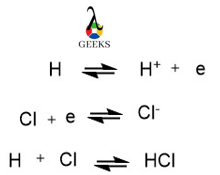
Is HCl + AgCl a Precipitation Reaction?
HCl + AgCl is not a precipitation reaction as the reaction reaches an equilibrium to the left side when sufficient chloride ions are present in the reaction.
Is HCl + AgCl a Reversible Reaction?
The HCl + AgCl reaction is reversible as the equilibrium is shifted backward so as to lower the concentration of chloride ions. The solubility of silver chloride in water decreases as more and more HCl is added as a result of common ion effect.
- AgCl = Ag+ + Cl–
- HCl = H+ + Cl–
Is HCl + AgCl a Double Displacement Reaction?
The reaction of HCl with AgCl is not a double displacement reaction as no multiple compounds are observed.
Conclusion
The reaction of Silver chloride with aqueous hydrochloric acid furnishes free chloride ions which, in excess, suppresses the dissolution of silver chloride in water. Silver chloride has very low solubility in water and HCl added just shifts equilibrium backward, as per Le Chatelier’s principle.

Hello….Neeloy here! I have pursued a Master’ in Chemistry and am currently a Subject Matter Expert in this community. Science and reasoning feed my curiosity and I love to express whatever I see, in my words. Quiz addict. Let’s connect at LinkedIn.