NaHCO3 is a weak base and for this reason, it can be reacted with concentrated acids like HBr. Let us explore the mechanism behind the reaction.
NaHCO3 or sodium bicarbonate is a weak base with having pH slightly above 7. So, it can react with a strong and concentrated form of acid like HBr. NaHCO3 has a monoclinic structure where central C is attached with one double bonded O, along with -OH group and -Ona whereas for HBr only one covalent bond is present.
The reaction between HBr and NaHCO3 does not require any kind of catalyst or temperature. Now we can discuss more the mechanism of the reaction like enthalpy, redox reaction, intermolecular force, conjugate pairs, etc with an explanation in the following part of the article.
1. What is the product of HBr and NaHCO3?
Sodium bromide and carbon dioxide are formed as major products along with water molecules when HBr and NaHCO3 were reacted together.
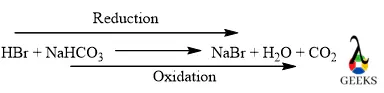
HBr + NaHCO3 = NaBr + CO2 + H2O
2. What type of reaction is HBr + NaHCO3?
HBr + NaHCO3 reaction is an example of a double displacement reaction, and a redox and precipitation reaction. It is also a salt metathesis reaction along with a hydrolysis reaction.
3. How to balance HBr + NaHCO3?
HBr + NaHCO3 = NaBr + CO2 + H2O, we have to balance the equation in the following way-
- First, we label all the reactants and products by A, B, C, D, and E as there are five different molecules obtained for this reaction and the reaction looks like this,
- A HBr + B NaHCO3 = C NaBr + D CO2 + E H2O
- Equating the coefficients for the same type of elements by rearranging them.
- After the rearrangement of coefficients of the same elements by their stoichiometric proportion, we get,
- H = A = B = 2E, Br = A = C, Na = B = C, C = B = D, O = 3B = 2D = E
- Using the Gaussian elimination and equating all the equations we get, A = 1, B = 1, C = 1, D =1, and E = 1
- The overall balanced equation will be,
- HBr + NaHCO3 = NaBr + CO2 + H2O
4. HBr + NaHCO3 titration
To estimate the strength of acid or carbonate quantity we can perform a titration between NaHCO3 and HBr.
Apparatus used
We need a burette, conical flask, burette holder, volumetric flask, and beakers for this titration.
Titre and titrant
HBr versus NaHCO3, HBr acts as a titrant taken in the burette and the molecule to be analyzed is NaHCO3 taken in a conical flask.
Indicator
The whole titration is done in an acidic medium or acidic pH so the best suitable indicator will be phenolphthalein which gives perfect results for this titration at given pH.
Procedure
The burette is filled with standardized HBr. NaHCO3 is taken in a conical flask along with respective indicators. HBr is added dropwise to the conical flask and the flask is shaken constantly. After a certain time, when the endpoint arrives, the indicator changes its color and the reaction is done.
5. HBr+ NaHCO3 net ionic equation
The net ionic equation between HBr + NaHCO3 is as follows,
H+(aq.) + Br–(aq.) + Na+(aq.) + 2H+(aq.) + CO32- (aq.) = Na+(aq.) + Br–(aq.) + H+(l) + OH–(l) + CO2(g)
- HBr will be ionized as proton and bromide as it is strong acid and electrolyte.
- After that NaHCO3 also dissociates into H+ ions and bicarbonate and then carbonate as a counter ion but dissociated in slowly as it is a weak base.
- In the product part, NaBr is ionized into Na+ and Br–as it is a strong electrolyte and salt.
- Water ionized into H+ and hydroxide ion.
- Carbon dioxide remains in the gaseous form and could not be dissociated.
6. HBr+ NaHCO3 conjugate pairs
In the reaction, HBr+ NaHCO3 conjugate pairs will be the corresponding de-protonated and protonated form of that particular species which are listed below-
- Conjugate pair of HBr = Br–
- Conjugate pair of CO32- = HCO3–
- Conjugate pair of HCO3–= H2CO3
7. HBr and NaHCO3 intermolecular forces
HBr+ NaHCO3 reaction has the following conjugate pairs,
- The intermolecular force present in HBr is the strong electrostatic force between protons and bromide ions.
- In NaHCO3 there are electronic interactions and coulumbic force present.
- In NaBr ionic interaction is present and for water H-bonding is present.
| Molecule | Acting force |
| HBr | Electrostatic, van der waal’s Dipole interaction |
| NaHCO3 | Strong electrostatic force and ionic interaction, Coulumbic force |
| NaBr | Electrostatic force, ionic interaction, |
| H2O | Covalent force, H-bonding |
| CO2 | Van der waal’s force, London dispersion force |
8. HBr + NaHCO3 reaction enthalpy
HBr + NaHCO3 reaction enthalpy is -12.43 KJ/mol which can be obtained by the formula: enthalpy of products – enthalpy of reactants. Here the change in enthalpy is negative.
| Molecule | Enthalpy (KJ/mol) |
| NaHCO3 | -947.7 |
| HBr | -36.23 |
| NaBr | -361.06 |
| H2O (water vapor) |
-241.8 |
| CO2 | -393.5 |
and Products
9. Is HBr + NaHCO3 a buffer solution?
In the reaction between HBr + NaHCO3, formed the buffer solution of the mixture of CO2 and H2O can control the pH even after adding a base or acid.
10. Is HBr + NaHCO3 a complete reaction?
The reaction between HBr + NaHCO3 is complete because it gives two major ones: an electrolytic salt and another carbon dioxide along with water as a by-product.
11. Is HBr + NaHCO3 an exothermic or endothermic reaction?
The reaction of HBr + NaHCO3 is exothermic in terms of thermodynamics first law. This reaction released more energy and temperature to the surroundings, where δH is always negative.
12. Is HBr + NaHCO3 a redox reaction?
HBr + NaHCO3 reaction is a redox reaction because in this reaction bromine gets reduced and also carbon gets oxidized. Where HBr acts as a reducing agent and NaHCO3 acts as an oxidizing agent.
HBr and NaHCO3 Reaction
13. Is HBr + NaHCO3 a precipitation reaction
The reaction between HBr + NaHCO3 is a precipitation reaction because sodium bromide gets precipitated in the solution at certain pH.
14. Is HBr + NaHCO3 reversible or irreversible reaction?
The reaction between HBr+ NaHCO3 is irreversible because it produced carbon dioxide. Due to the production of the gaseous molecule, the entropy of the reaction increased, and the equilibrium shifts towards the right-hand side only or forward directions.
HBr + NaHCO3 —-> NaBr + CO2↑ + H2O
15. Is HBr + NaHCO3 displacement reaction?
The reaction between HBr+ NaHCO3 is an example of a double displacement reaction. Because in the above reaction H+ was displaced by Na+ from HBr and Na is also displaced by H+ and attached to Br.

Conclusion
The reaction between HBr and NaHCO3 is important because it can produce carbon dioxide. So, the reaction is very important in the industrial aspect. The reaction is also important for the production of sodium bromide salt.

Hi……I am Biswarup Chandra Dey, I have completed my Master’s in Chemistry from the Central University of Punjab. My area of specialization is Inorganic Chemistry. Chemistry is not all about reading line by line and memorizing, it is a concept to understand in an easy way and here I am sharing with you the concept about chemistry which I learn because knowledge is worth to share it.