Magnesium nitride (Mg3N2) is an inorganic substance that appears greenish-yellow powder. Watch how it responds to sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
A binary ionic chemical, Magnesium nitride is also referred to as azanidylidenemagnesium. Magnesium hydroxide and ammonia gas are produced after its reaction with water. Each magnesium atom has an oxidation state of +2, and each nitrogen atom has an oxidation state of –3 in Mg3N2. It reacts with H2SO4.
This post will examine some intriguing information about the interaction between H2SO4 and Mg3N2.
1. What is the product of H2SO4 and Mg3N2?
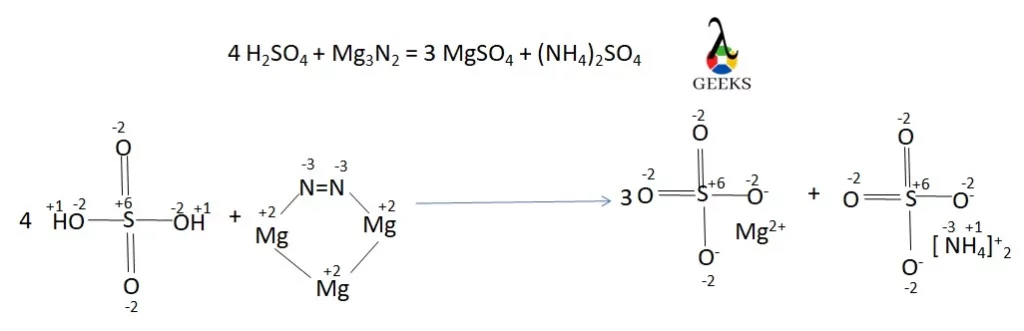
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 result into Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) and Ammonium etraoxosulfate(VI) ((NH4)2SO4) when they react. The reaction is as follows,
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 -> MgSO4 + (NH4)2SO4
2. What type of reaction is H2SO4 + Mg3N2?
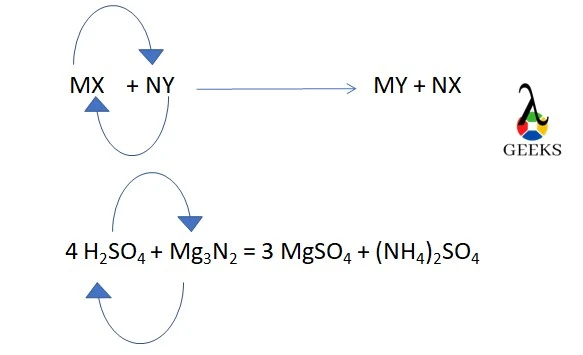
H2SO4 +Mg3N2 is a twofold displacement reaction, also referred to as a metathesis reaction.
3. How to balance H2SO4 + Mg3N2?
The H, S, O, Mg, and N atoms must all be present in equal amounts on each side of the equation for H2SO4 and Mg3N2 reaction to being balanced.
- First, we label each of the four molecules—A, B, C, and D—because there are four. The reply looks like this:
- A H2SO4 + B Mg3N2 = C MgSO4 + D (NH4)2SO4
- The number of coefficients specified as alphabets in the reactants and products is now determined using the proper values.
| Element | Reaction side | Product side |
| Hydrogen | 2A+0B | 0C+8D |
| Sulfur | 1A+0B | 1C+1D |
| Oxygen | 4A+0B | 4C +4D |
| Magnesium | 0A +3B | 1C +0D |
| Nitrogen | 0A+2B | 0C+2D |
- The coefficient and variables required to balance the equation are obtained using the Gaussian elimination approach in Step 3.
- A= 4(H2SO4), B= 1(Mg3N2), C= 3(MgSO4), D= 1 (NH4)2SO4
- The reactant and product sides now contain an equal number of each element.
| Element | Reaction side | Product side |
| Hydrogen | 8 | 8 |
| Sulfur | 4 | 4 |
| Oxygen | 16 | 16 |
| Magnesium | 3 | 3 |
| Nitrogen | 2 | 2 |
- The reaction between H2SO4 and Mg3N2 has a balanced equation in step four, which is
- 4 H2SO4 + Mg3N2 =3 MgSO4 + (NH4)2SO4
4. H2SO4 + Mg3N2 titration
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 direct titration cannot be predicted despite the fact that H2SO4 is a potent acid. However, it does suggest that redox titration may be possible in the presence of some abnormalities.
5. H2SO4+ Mg3N2 net ionic equation
The net ionic equation for the reaction of H2SO4 + Mg3N2 is,
8H+(l) + 2N3-(l) = 2(NH4)+1(l)
- Each compound’s phase must be considered and balanced in a molecular equation.
- 4 H2SO4 (l) + Mg3N2 (l) =3 MgSO4 (l)+ (NH4)2SO4 (l)
- The aqueous salts or compounds in the equation must be changed into ions. Only the strong electrolytes should be dissolved since the weak electrolytes can completely dissociate.
- 8H++4SO42-+ 3Mg2++2N3- = 3Mg2+ + 3 SO42-+ 2NH4+ + SO42-
- We remove the spectator ions to identify the species participating in the reaction.
- This is the net ionic equation: 8H+(l) + 2N3-(l) = 2(NH4)+1(l)
6. H2SO4 + Mg3N2 conjugate pairs
H2SO4+ Mg3N2 reaction has the following conjugate pairs,
- H2SO4‘s conjugate base is HSO4–.
7. H2SO4 and Mg3N2 intermolecular forces
Intermolecular forces exist between H2SO4+ Mg3N2 are:
- H2SO4 exhibits hydrogen bonding due of the acidic protons connected to the oxygen.
- The permanent dipole in H2SO4 causes it to exhibit dipole-dipole interaction.
- H2SO4 exhibits van der Waals dispersion forces due to its asymmetrical structure.
- Mg3N2 exhibits metallic bonding since it has a metallic Mg-Mg connection.
- Additionally, Mg3N2 exhibits intermolecular ionic and covalent forces.
| Element | Van der Waals’ radius (Å) |
| Hydrogen | 1.20 |
| Sulfur | 1.80 |
| Oxygen | 1.52 |
| Magnesium | 1.73 |
| Nitrogen | 1.09 |
8. H2SO4 + Mg3N2 reaction enthalpy
The reaction enthalpy of H2SO4 + Mg3N2 is -2198.1 KJ/mol
| Compound | Moles | Enthalpy of formation, ΔH0f (KJ/mol) |
| H2SO4 | 4 | -814 |
| Mg3N2 | 1 | 457.2 |
| MgSO4 | 3 | -1272 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 1 | -1180.9 |
- The standard enthalpy of a reaction can be calculated using the formula below:
- The formula is, ΔH0f (reaction) = ΣΔH0f (product) – ΣΔH0f (reactants)
- Thus, enthalpy change = [3*(-1272) + 1*(-1180.9)] – [4*(-814) + 1*(457.2)] KJ/mol = -2198.1 KJ/mol
9. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 a buffer solution?
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 reaction won’t produce a buffer solution since H2SO4 is a strong acid.
10. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 a complete reaction?
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 is a complete reaction, as it indicates the formation of magnesium sulfate and ammonium tetraoxosulfate(VI), two stable molecules.
11. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 an exothermic or endothermic reaction?
H2SO4 + Mg3N2‘s reaction is exothermic because the process causes heat to be released into the surrounding air.
12. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 a redox reaction?
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 reaction has no redox character. Throughout the course of the reaction, the oxidation state of each atom remains unchanged.
13. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 a precipitation reaction?
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 reaction does not result in precipitation because it yields two ionic compounds still soluble in the reaction medium. There is no precipitate made.
14. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 a reversible or irreversible reaction?
H2SO4+ Mg3N2 is an irreversible reaction because the products are not converted back into the reactants under the same circumstances.
15. Is H2SO4 + Mg3N2 a displacement reaction?
H2SO4 + Mg3N2 when interact, double displacement happens. Magnesium removes the protons from the H2SO4 molecules to create MgSO4, and H2SO4 replaces Mg in Mg3N2 to create (NH4)2SO4.
Conclusion
Magnesium sulfate and Ammonium tetraoxosulfate(VI), two commonly used inorganic salts, were synthesized by mixing H2SO4 and Mg3N2. Mg3N2 are well-known catalyzing polymer to produce cross-linking polymers. MgSO4, on the other hand, is essential to remove sulfur from steel and iron.

Hey readers, I am Ishita Ghosh. I have done my Master’s in Chemistry. My area of specialization is Inorganic Chemistry. The true way to comprehend chemistry is to understand it from its grassroots level. My effort is to share every bit of knowledge in chemistry I have so that it helps you for a better grasp on this subject.