Magnesium silicide (Mg2Si) is a crystalline solid inorganic compound. Let’s see its reaction with Sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
Mg2Si is water-insoluble and denser than water. It forms a face-centered cubic antifluorite structure. Si4- ion can be thought of as the main component of magnesium silicide. It reacts with acid. H2SO4 is highly soluble in water. It is available in oily, liquid form. It is one of the strongest acids available.
In this article, we shall discuss the reaction between H2SO4 + Mg2Si, and some interesting facts.
1. What is the product of H2SO4 and Mg2Si?
Silicon tetrahydride (SiH4), also known as Silane, and Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) are formed as products by the reaction between H2SO4 and Mg2Si. The reaction is,
H2SO4 + Mg2Si → SiH4 + MgSO4
2. What type of reaction is H2SO4 + Mg2Si?
The type of reaction between H2SO4 and Mg2Si is a double displacement reaction, else known as Metathesis reaction.
3. How to balance H2SO4 + Mg2Si?
To balance the equation between H2SO4 and Mg2Si, we must determine whether an equal number of individual atoms (H, S, O, Mg, and Si) are present on both the reactant and product sides.
- Since four molecules are present, we first designate each one as A, B, C, and D.
- This is how the response appears: A H2SO4 + B Mg2Si = C SiH4 + D MgSO4.
- Using the appropriate values, we now figure out how many coefficients are listed in the reactants and products as alphabets.
| Element | Reaction side | Product side |
| Hydrogen | 2A+ 0B | 4C+0D |
| Sulfur | 1A+ 0B | 0C+1D |
| Oxygen | 4A+0B | 0C+4D |
| Magnesium | 0A+2B | 0C+1D |
| Silicon | 0A+1B | 1C+0D |
- The Gaussian elimination procedure is used in Step 3 to get the coefficient and variables needed to balance the equation.
- A= 2(H2SO4), B= 1(Mg2Si), C= 1(SiH4), D= 2(MgSO4)
- Now, an equal number of each element is present on both the reactant and product side.
| Element | Reaction side | Product side |
| Hydrogen | 4 | 4 |
| Sulfur | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 |
| Magnesium | 2 | 2 |
| Silicon | 1 | 1 |
- The balanced equation of the reaction between H2SO4 and Mg2Si is,
- 2H2SO4+ Mg2Si = SiH4 + 2MgSO4.
4. H2SO4 + Mg2Si titration
Titration between H2SO4 and Mg2Si cannot be predicted as acid-base reaction though H2SO4 is a strong acid. Mg2Si does not act as a base in the reaction. It does, however, indicate the possibility of redox titration with certain anomalies.
5. H2SO4+ Mg2Si net ionic equation
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction’s net ionic equation is,
4H+(aq) + Si4-(s) = Si(4+)H4(-1) (g)
- A molecular equation needs to be balanced and consider each compound’s phase.
- 2H2SO4(aq) + Mg2Si(s) → SiH4(g) +2MgSO4(s)
- It is necessary to convert the aqueous salts or chemicals in the equation into ions. Because they can entirely dissociate, only the strong electrolytes should be broken down.
- 4H++2SO42-+ 2Mg2++Si4- = Si4++4H– + 2Mg2+ + 2SO42-
- We eliminate the spectator ions to reveal the species that are truly involved in the reaction.
- The net ionic equation is,
- 4H+(aq) + Si4-(s) = Si(4+)H4(-1)(g)
6. H2SO4 + Mg2Si conjugate pairs
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction has the following conjugate pairs,
- HSO4– is H2SO4’s conjugate base.
- Si4- is SiH4‘s conjugate base.
7. H2SO4 and Mg2Si intermolecular forces
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction has the following intermolecular forces,
| Molecule | Intermolecular forces |
| H2SO4 | Dipole-dipole, hydrogen bond, Van der Waal’s |
| Mg2Si | Complex ionic bond, metallic bond |
| SiH4 | Covalent bond |
| MgSO4 | Ionic bond |
8. H2SO4 + Mg2Si reaction enthalpy
The reaction enthalpy of H2SO4 + Mg2Si is -860. 49 KJ/ mol.
| Compound | Moles | Enthalpy of formation, ΔH0f (KJ/mol) |
| H2SO4 | 2 | -814 |
| Mg2Si | 1 | -21.20 |
| SiH4 | 1 | 34.31 |
| MgSO4 | 2 | -1272 |
- The following formula is used to compute a reaction’s standard enthalpy,
- The formula is, ΔH0f (reaction) = ΣΔH0f (product) – ΣΔH0f (reactants)
- Thus, enthalpy change = [2*(-1272) + 1*(34.31)] – [2*(-814) + 1*(-21.20)] KJ/mol= -860.49 KJ/mol
9. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si a buffer solution
H2SO4 + Mg2Si will not create a buffer solution as strong acid H2SO4 is present.
10. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si a complete reaction
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction is complete because it results in Silane and Magnesium sulfate, two stable molecules.
11. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si an exothermic or endothermic reaction
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction is exothermic because it generates heat in the environment while creating the result.
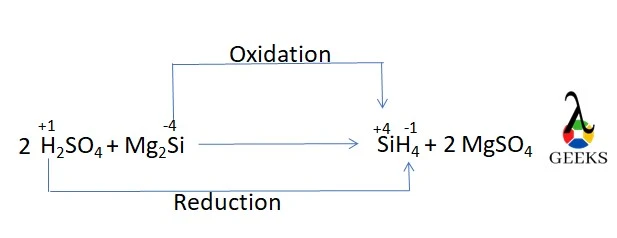
12. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si a redox reaction
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction is redox in nature due to the change in silicon ions’ and hydrogen ions’ oxidation states on the reactant and product sides.
13. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si a precipitation reaction
H2SO4 + Mg2Si reaction is not a precipitation process since no precipitate is produced.
14. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si a reversible or irreversible reaction
H2SO4 and Mg2Si reaction is an irreversible reaction due to the fact that the products produced do not revert to the reactants under the same conditions.
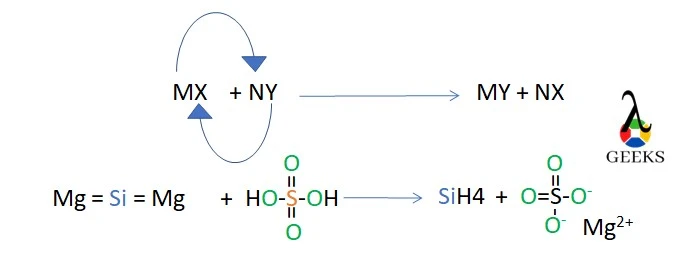
15. Is H2SO4 + Mg2Si a displacement reaction
Double displacement occurs when H2SO4 and Mg2Si react. Sulfate ions are removed from the H2SO4 molecules and silicon ions from the Mg2Si molecule to create Silane and Magnesium sulfate.
Conclusion
Silane and magnesium sulfate, employed in both commercial and scientific settings, were synthesized by mixing H2SO4 and Mg2Si. Silane is a component of fiberglass that enhances its electrical and mechanical qualities. Magnesium sulfate is used to control viscosity in liquid soaps and detergents.

Hey readers, I am Ishita Ghosh. I have done my Master’s in Chemistry. My area of specialization is Inorganic Chemistry. The true way to comprehend chemistry is to understand it from its grassroots level. My effort is to share every bit of knowledge in chemistry I have so that it helps you for a better grasp on this subject.