Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a highly corrosive and versatile chemical compound with a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. Its density is a crucial factor in understanding its behavior and properties, as it can vary significantly with concentration. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of H2SO4 density, providing a wealth of technical details and practical insights for physics students and professionals.
Understanding the Density of Sulfuric Acid
The density of sulfuric acid is a measure of its mass per unit volume, typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). This value is not constant and can change depending on the concentration of the acid solution. The density of H2SO4 is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities or other dissolved substances.
Factors Affecting Sulfuric Acid Density
-
Concentration: The concentration of sulfuric acid is the primary factor that determines its density. As the concentration of H2SO4 increases, the density also increases. This relationship is not linear, and the density reaches a maximum at around 87% concentration.
-
Temperature: The density of sulfuric acid is inversely proportional to temperature. As the temperature increases, the density decreases due to the expansion of the liquid.
-
Pressure: The density of sulfuric acid is slightly affected by pressure. As the pressure increases, the density also increases, but the effect is relatively small compared to the influence of concentration and temperature.
-
Impurities: The presence of impurities, such as water or other dissolved substances, can affect the density of sulfuric acid. The addition of impurities can either increase or decrease the density, depending on the nature and concentration of the impurities.
Density Measurement Techniques
Accurate measurement of sulfuric acid density is crucial for various applications, such as determining the concentration of the solution, monitoring industrial processes, and ensuring product quality. Several techniques are available for measuring the density of H2SO4, including:
-
Digital Density Meters: These instruments use the principle of oscillating U-tube technology to measure the density of the sample. The sample is introduced into a U-shaped glass or metal tube, and the change in the tube’s oscillation frequency is used to calculate the density.
-
Hydrometer Measurements: Hydrometers are simple and inexpensive devices that measure the density of liquids by floating in the sample. The depth to which the hydrometer sinks is related to the density of the liquid.
-
Pycnometer Measurements: Pycnometers are calibrated glass vessels used to determine the density of liquids by measuring the mass of a known volume of the sample.
-
Gravimetric Analysis: This method involves weighing a known volume of the sulfuric acid sample and calculating the density based on the mass and volume.
Density-Concentration Relationship
The relationship between the density and concentration of sulfuric acid is complex and non-linear. The density of H2SO4 solutions can be determined using density tables or empirical equations, which provide the density values for different concentrations at a specific temperature.
One such equation, known as the Timmermans equation, can be used to calculate the density of sulfuric acid solutions:
ρ = 1000 + 6.8 × C - 0.228 × C^2 + 0.00045 × C^3
Where:
– ρ is the density of the sulfuric acid solution in g/cm³
– C is the concentration of the sulfuric acid solution in %w/w (weight percentage)
This equation is valid for concentrations ranging from 0% to 100% and temperatures between 0°C and 100°C.
Density Tables and Data
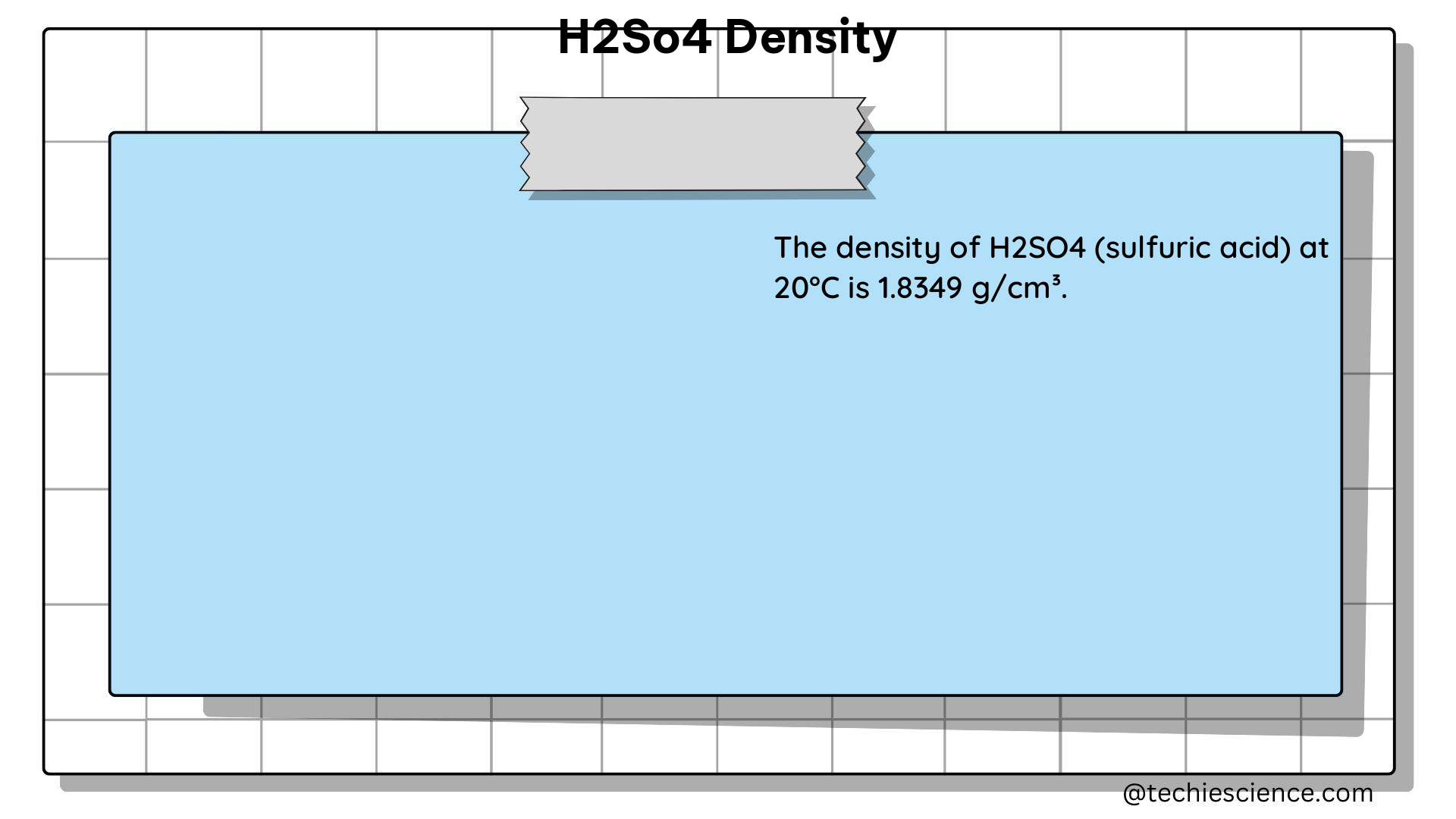
To provide a more comprehensive understanding of sulfuric acid density, here are some detailed data points and tables:
Density of Sulfuric Acid at Different Concentrations and Temperatures
| Concentration (% w/w) | Density (g/cm³) at 20°C | Density (g/cm³) at 25°C |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | 1.0725 | 1.0650 |
| 20% | 1.1400 | 1.1320 |
| 30% | 1.2200 | 1.2110 |
| 40% | 1.3050 | 1.2950 |
| 50% | 1.3950 | 1.3840 |
| 60% | 1.4900 | 1.4780 |
| 70% | 1.5900 | 1.5770 |
| 80% | 1.6950 | 1.6810 |
| 90% | 1.8200 | 1.8050 |
| 98% | 1.8400 | 1.8250 |
Density of Sulfuric Acid at Different Temperatures (98% Concentration)
| Temperature (°C) | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1.8846 |
| 10 | 1.8573 |
| 20 | 1.8300 |
| 30 | 1.8027 |
| 40 | 1.7754 |
| 50 | 1.7481 |
| 60 | 1.7208 |
| 70 | 1.6935 |
| 80 | 1.6662 |
| 90 | 1.6389 |
| 100 | 1.6116 |
Density of Sulfuric Acid Hydrates
Sulfuric acid can form different hydrates, which can affect its density. The density of some common sulfuric acid hydrates is as follows:
| Hydrate Formula | Density (g/cm³) at 20°C |
|---|---|
| H2SO4·H2O | 1.3315 |
| H2SO4·2H2O | 1.2305 |
| H2SO4·3H2O | 1.1715 |
Practical Applications and Considerations
The density of sulfuric acid is crucial in various industrial and scientific applications, including:
-
Concentration Determination: The density of a sulfuric acid solution can be used to determine its concentration, which is essential for quality control, process monitoring, and product formulation.
-
Acid Handling and Storage: The density of sulfuric acid is important for determining the volume and weight of the acid, which is crucial for safe handling, transportation, and storage.
-
Battery Manufacturing: The density of sulfuric acid is a critical parameter in the production and maintenance of lead-acid batteries, as it affects the battery’s performance and lifespan.
-
Environmental Monitoring: The density of sulfuric acid is used to monitor and control the emission of sulfuric acid vapors in industrial processes, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
-
Chemical Reactions and Processes: The density of sulfuric acid is a crucial factor in various chemical reactions and processes, such as the production of fertilizers, dyes, and explosives.
When working with sulfuric acid, it is essential to consider the density and concentration of the solution, as well as the potential hazards associated with this highly corrosive substance. Proper safety precautions, personal protective equipment, and handling procedures must be followed to ensure the safety of personnel and the environment.
Conclusion
The density of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a complex and crucial parameter that plays a vital role in various industrial and scientific applications. This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of the factors affecting sulfuric acid density, the techniques used for its measurement, and the practical implications of understanding this property.
By mastering the concepts and data presented in this guide, physics students and professionals can enhance their understanding of sulfuric acid behavior, improve process efficiency, and ensure the safe handling and storage of this versatile yet hazardous chemical.
References
- Anton Paar, “Concentration determination by means of density measurement,” accessed on June 18, 2024, https://wiki.anton-paar.com/at-de/konzentrationsbestimmung-mittels-dichtemessung/
- DCCEEW, “Sulfuric acid,” accessed on June 18, 2024, https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/protection/npi/substances/fact-sheets/sulfuric-acid
- Steffen’s Chemistry Pages, “Density of sulfuric acid and sulfur trioxide,” accessed on June 18, 2024, https://wissen.science-and-fun.de/chemistry/chemistry/density-tables/density-of-sulfuric-acid-and-sulfur-trioxide/
- Anton Paar, “Measuring the density and specific gravity of battery acid in lead acid batteries,” accessed on June 18, 2024, https://wiki.anton-paar.com/us-en/density-and-density-measurement/measuring-the-density-and-specific-gravity-of-battery-acid-in-lead-acid-batteries/
- EPA, “Method 8a – Determination of Sulfuric Acid Vapor,” accessed on June 18, 2024, https://www3.epa.gov/ttnemc01/ctm/ctm-013.pdf

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.