In this article we want to discuss things related functional isomers example with detailed facts as well.
Isomers are a type of compounds which possess same molecular formula but distribution of atoms are different in space. . Functional isomer is those organic as well as inorganic compound which possess same formula but have different functional group in them. Functional isomer is a part of structural isomer.
Functional isomers example are given below:
C2H6O
C2H6O has two functional isomers example. One is di-methyl ether (CH3OCH3) and other is ethanol (CH3CH2OH). In di-methyl ether the functional group is ether i.e. -C-O-C- linkage. Di-methyl ether also known as methoxymethane. In ethanol the functional group is hydroxyl group i.e. –OH group.
As two isomer differ in their boiling point these 2 isomer can be distinguished easily. Due to presence of OH group in ethanol there occurs intermolecular H bonding between the molecules of ethanol. To separate them large amount of energy is required for this it has high boiling point.
But in case of dimethyl ether due to absence of OH group no H bonding takes place between them so that it has lower boiling point. As ethanol is more polar than dimethyl ether, these 2 isomer are identified by their polarity. Also ethanol is capable of forming intermolecular H bonding with H2O molecule it is soluble in water but dimethyl ether can’t form H bonding with water. It is less soluble in water.

C3H6O
C3H6O has two functional isomers example. One is propanal (CH3CH2CHO) and the other is propanone (CH3COCH3). In propanal the functional group is –CHO i.e. aldehyde and in propanone the functional group is –CO i.e. ketone. Propanal and propanone can be differentiate from each other by a chemical reaction named haloform reaction.
when both the compound are reacted with NaOH and I2 due to presence of α-H atom in propanone it gives the yellow precipitate of CHI3 but propanal does not give this test due to the absence of α- H atom. Nucleophilic addition reaction is fast with propanal than propanone due to steric as well electronic factor.
Carbonyl carbon is less sterically hindered and more electrophilic in propanal than propanone. Propanone has higher boiling point than propanone because in propanone the carbonyl group is more polarized than that of propanal. For this dipole-dipole force of attraction is higher in propanone than propanal and boiling point is higher in propanone than propanal.

C2H4O2
C2H4O2 has two functional isomers example. One is acetic acid (CH3COOH) and the other is methyl formate (HCOOCH3). In acetic acid the functional group is acid i.e. –COOH group. In methyl formate the functional isomer is ester i.e. –COOR group.
Both isomer have same molecular formula but different functional group and have different physical and chemical properties. By their boiling point these 2 isomer can be separated from each other . Acetic acid has higher boiling point than methyl formate because in acetic acid there occurs intramolecular H bonding which does not occur in methyl formate due to absence of –OH group.
For that reason to separate acetic acid molecule from each other large amount of energy is required. If both the isomer are reacted with NaHCO3 in presence of small amount of heat the isomer in which we see the effervescence of CO2 gas is acetic acid. By this chemical method we can distinguish between an acid and an ester.
They can also be differentiating by their dipole moment values. Acetic acid has higher dipole moment value than methyl formate. For this higher polarity of acetic acid it is more soluble in water than methyl formate.

C3H9N
C3H9N exist in 3 functional isomers example. These are propan-1-amine (CH3CH2CH2NH2), N-methyl ethanamine (CH3CH2NHCH3), N,N- dimethyl methanamine [(CH3)3N]. Propane-1-amine is 10 amine, N-methyl ethanamine is 20 amine, N,N-dimethyl methanamine is 30 amine. All these have same molecular formula but have different functional groups.
These three amines are differentiating from each other by Hinsberg’s reagent. When reacts with hinsberg’s reagent propan-1-amine give a sulphonamide which is readily soluble in alkali. N-methyl ethanamine also give a sulphonamide which is insoluble in nature. But N,N-dimethyl methanamine does not give this test due to absence of H atom on N atom, it can’t be neutralized further.
They can also be distinguished by their boiling point. The boiling point order is: propan-1-amine>N-methyl ethanamine>N,N –dimethyl methanamine. Also their solubility is different in water. Propan-1-amine is highly soluble in nature and N,N-dimethyl Methanamine is least soluble in water and 20 amine lies between them.
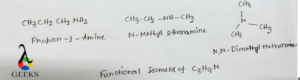
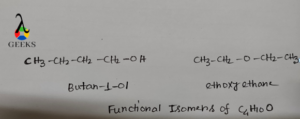
C4H10O
C4H10O exist in two functional isomers example. One is butan-1-ol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH)and the other is ethoxyethane (CH3CH2OCH2CH3). In butan-1-ol the functional group is –OH group and in ethoxyethane the functional group is ether i.e. –C-O-C- linkage.
These two isomer can be isolated from each other by the difference in their boiling point. Due to presence of –OH group there occurs intermolecular H bonding between the molecules of butan-1-ol. As to separate them from each other large amount of energy is required.
For this reason it has higher boilling point than ethoxyethane where no H bonding occurs due to absence of –OH group. By reacted the two isomer with PCl5 butan-1-ol gives the precipitate of alkyl chloride whereas ether does not give the same. By this chemical method we also differentiate these 2 isomer.
Also butan-1-ol is soluble in water where as ethoxyethane is insoluble in water. As because butan-1-ol forms H bonding with water but ethoxyethane does not.
C4H8O2
C4H8O2 has 2 functional isomers example. One is butanoic acid (CH3CH2CH2COOH) and the other is methyl propionate (CH3CH2COOCH3). In butanoic acid the functional group is acid i.e. –COOH group and methyl propionate has functional group ester i.e. –COOR group.
As their boiling point is different 2 isomers can be distinguished separately. Butanoic acid has higher boiling point than methyl propionate. This is due to the presence of intramolecular H bonding in former compound which does not arises in case of latter compound due to absence of –OH group.
That is why to separate the molecules of butanoic acid large amount of energy is required so that it has higher boiling point than methyl propionate. when 2 isomers are reacted with NaHCO3 in heat butanoic acid gives the effervescence of CO2 gas but methyl propionate does not give this test.
By this chemical method we can distinguish an acid and an ester. Butanoic acid has higher boiling point than methyl propionate due to the higher polarity of acid than ester.

C4H8O
C4H8O has 2 functional isomers example. One is butanal (CH3CH2CH2CHO)and the other is butanone (CH3COCH2CH3). In butanal the functional group is –CHO i.e. aldehyde and butanone has ketonic functional group i.e. –CO.
These 2 functional isomers can be differentiate from each other by a chemical reaction named haloform reaction. When both the isomers are reacted with NaOH and I2 due to presence of α-H atom butanone gives yellow precipitate of CHI3 but butanal does not give this test due to absence of α-H atom.
Nucleophilic addition reaction occurs at a faster rate in butanal due to steric as well as electronic factor. Carbonyl carbon is less sterically hindered and more electrophilic in butanal than butanone. Butanone has higher boiling point than butanal because in butanone the carbonyl group is more polarized than that of butanal.
For this dipole-dipole force of attraction is higher in butanone than butanal and boiling point is higher in butanone than butanal.
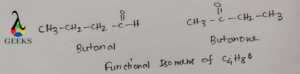

Hi….I am Susanta Maity. I have completed my Masters from Vidyasagar university with a specialization in organic chemistry.
I love to write complicated Chemistry concepts in understandable and simple words.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn: