Summary
The field of view (FOV) in microscopy is a critical parameter that determines the size of the observable area. It is calculated using the formula: Field of View = Field Number (FN) ÷ Objective Magnification. This guide provides a detailed explanation of the field of view formula, its theoretical background, measurable data, figures, data points, physics formulas, examples, and numerical problems to help physics students understand this concept thoroughly.
Understanding the Field of View Formula
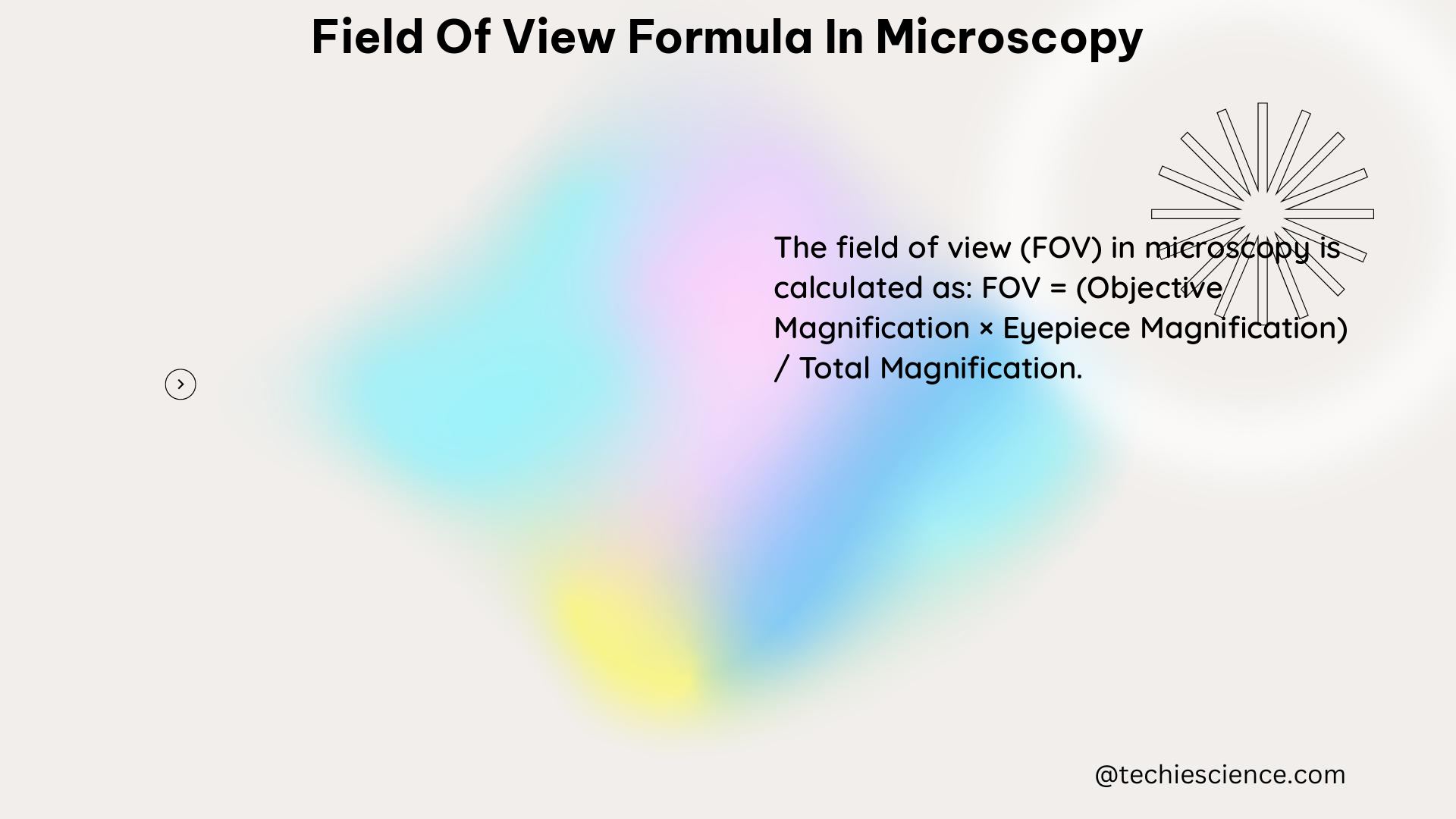
The field of view (FOV) in microscopy is the diameter of the observable area that can be seen through the microscope’s eyepiece. This parameter is crucial in determining the size of the sample that can be viewed at a given magnification. The field of view formula is:
Field of View = Field Number (FN) ÷ Objective Magnification
Where:
– Field Number (FN): The diameter of the field view in millimeters, measured at the intermediate image plane. This value is typically listed on the microscope eyepiece and ranges from 7 mm to 26 mm, depending on the eyepiece magnification.
– Objective Magnification: The magnification power of the objective lens, which can vary from 10X to 100X or higher.
For example, if the field number is 25 mm and the objective magnification is 100X, the field of view would be:
Field of View = 25 mm ÷ 100 = 0.25 mm
Auxiliary Lens Magnification
If an auxiliary lens is used on a stereo microscope, the magnification factor of this lens should also be included in the equation by multiplying it with the objective magnification:
Field of View = FN ÷ (Objective Magnification x Auxiliary Lens Magnification)
For instance, if the eyepiece reads 10X/22 and the magnification of the objective lens is 40, the total magnification would be 10 × 40 = 400. Then, the field of view would be:
Field of View = 22 mm ÷ 400 = 0.055 mm
Theoretical Explanation
The field of view is inversely proportional to the magnification. Higher magnifications result in smaller fields of view, while lower magnifications result in larger fields of view. This is because higher magnifications focus on smaller areas, while lower magnifications capture larger areas.
Measurable Data
- Field Number (FN): Typically listed on the microscope eyepiece, it ranges from 7 mm to 26 mm depending on the eyepiece magnification.
- Objective Magnification: Varies from 10X to 100X or higher, depending on the objective lens.
- Field of View (FOV): Calculated using the formula, it can range from 0.0125 mm to 0.25 mm or more, depending on the magnification and field number.
Figures and Data Points
Field Number (FN) vs. Eyepiece Magnification:
| Eyepiece Magnification | Field Number (FN) |
| ———————- | —————- |
| 5x | 26 mm |
| 10x | 22 mm |
| 30x | 7 mm |
Field of View (FOV) vs. Magnification:
| Magnification | Field of View (FOV) |
| ————- | ——————- |
| 100X | 0.25 mm |
| 400X | 0.0625 mm |
| 1000X | 0.025 mm |
Physics Formula
The field of view formula is based on the principle of magnification, where the diameter of the field view is divided by the magnification power to obtain the field of view.
Examples and Numerical Problems
- Calculate the field of view if the field number is 20 mm and the objective magnification is 50X.
-
FOV = 20 mm ÷ 50 = 0.4 mm
-
Calculate the field of view if the eyepiece reads 15X/18 and the objective magnification is 30X.
- Total magnification = 15 × 30 = 450
- FOV = 18 mm ÷ 450 = 0.04 mm
Reference Links
- Microscope World – How to Calculate Microscope Field of View
- Rice University – Measurement with the Light Microscope
- AmScope – How To Calculate Field of View for Your Microscope
- National Center for Biotechnology Information – Increasing a microscope’s effective field of view via overlapped imaging and machine learning
- Microscope International – How to Estimate the Field of View of a Microscope

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.