Ferric chloride (FeCl3) is a highly soluble compound in water, as indicated by its solubility rules and solubility chart. The solubility of FeCl3 in water is a crucial factor in various industrial and scientific applications, from water treatment to electroplating. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate details of FeCl3 solubility, exploring its underlying principles, quantitative data, and practical implications.
Understanding FeCl3 Solubility: Solubility Rules and Solubility Charts
The solubility of a compound is governed by a set of well-established solubility rules. These rules provide a general framework for predicting the solubility of ionic compounds in water. According to the solubility rules, chloride ion compounds, such as FeCl3, are generally soluble in water, with a few exceptions. Since iron (Fe) is not one of the exceptions, FeCl3 is expected to be soluble in water.
To further confirm the solubility of FeCl3, we can refer to solubility charts. These charts graphically represent the solubility of various ionic compounds based on the charges of the constituent ions. When we locate FeCl3 on the solubility chart, we find it situated in the soluble region, where the iron (Fe) has a three-plus ionic charge and the chloride (Cl) has a one-minus ionic charge.
Quantitative Data on FeCl3 Solubility
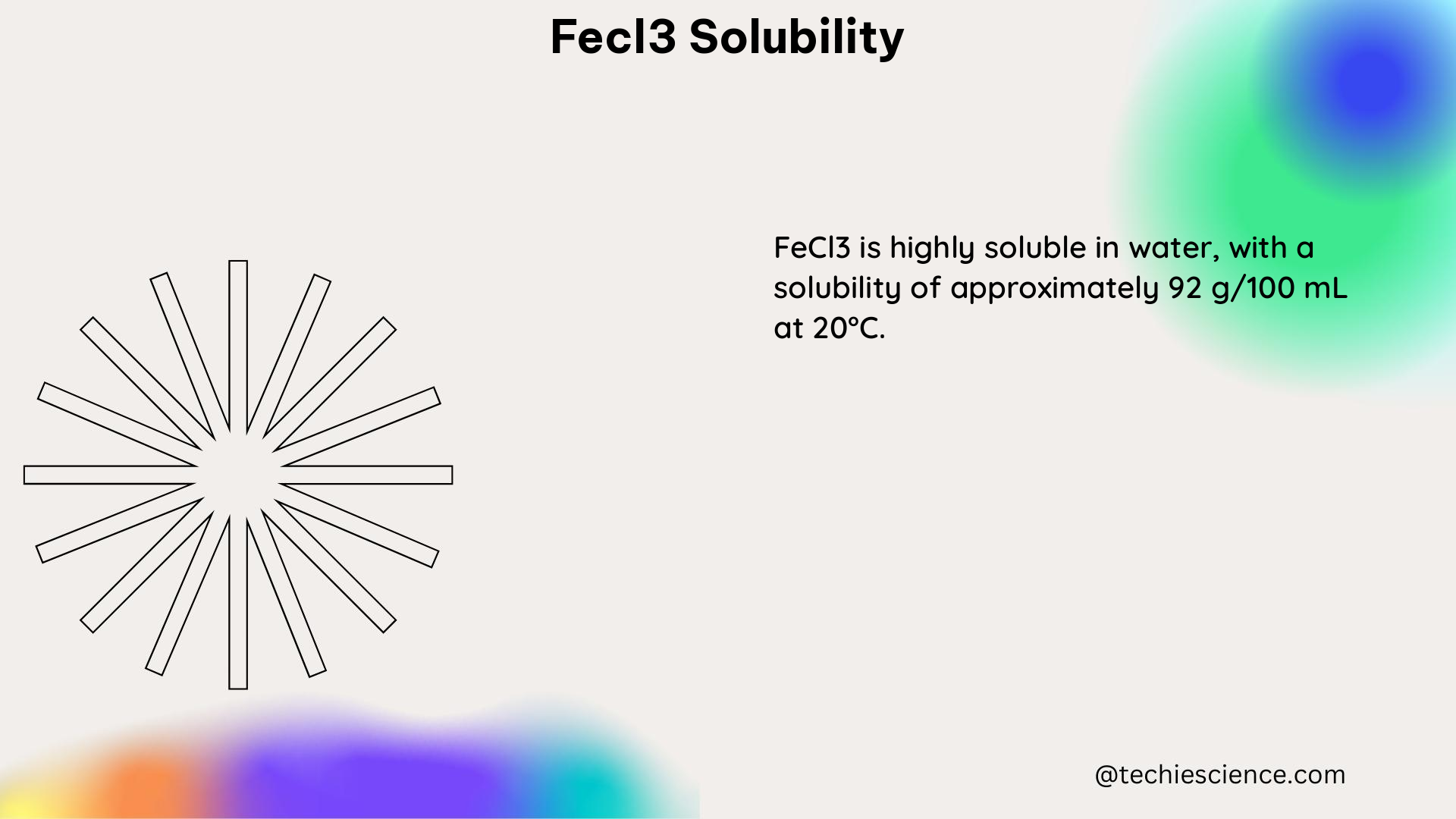
While the solubility rules and charts indicate that FeCl3 is highly soluble in water, the exact quantitative data on its solubility is essential for practical applications. According to the information provided on PubChem, FeCl3 is slightly soluble in water, but the specific solubility value or concentration is not explicitly stated.
To obtain more detailed quantitative data on FeCl3 solubility, we need to refer to specialized literature or conduct experiments. Some key data points that would be valuable to know include:
- Solubility Curve: The solubility curve of FeCl3 in water, which would show the relationship between the solubility and temperature or other variables.
- Solubility Constant (Ksp): The solubility product constant (Ksp) of FeCl3, which is a measure of the equilibrium solubility of the compound.
- Solubility Limit: The maximum concentration of FeCl3 that can be dissolved in water at a given temperature and pressure.
- Solubility in Other Solvents: The solubility of FeCl3 in other solvents, such as organic solvents, which may be relevant for specific applications.
By gathering this quantitative data, we can gain a deeper understanding of the solubility behavior of FeCl3 and its practical implications.
Factors Affecting FeCl3 Solubility
The solubility of FeCl3 in water can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Temperature: The solubility of FeCl3 is typically temperature-dependent, with higher temperatures generally increasing the solubility.
- pH: The pH of the solution can affect the speciation and solubility of FeCl3. In acidic environments, the solubility may be enhanced due to the formation of soluble iron-chloride complexes.
- Ionic Strength: The presence of other ions in the solution, such as sodium or chloride ions, can influence the solubility of FeCl3 through ionic interactions and the formation of complex species.
- Pressure: Changes in pressure can also affect the solubility of FeCl3, although the impact is typically less significant compared to temperature and pH.
Understanding the influence of these factors is crucial for optimizing the solubility of FeCl3 in various applications, such as water treatment, electroplating, and chemical synthesis.
Applications of FeCl3 Solubility
The solubility of FeCl3 in water has numerous practical applications, including:
- Water Treatment: FeCl3 is widely used as a coagulant in water treatment processes, where its solubility allows it to effectively remove suspended particles, organic matter, and other contaminants from water.
- Electroplating: FeCl3 is employed as an etching agent in the electroplating industry, where its solubility enables the controlled removal of metal layers from surfaces.
- Chemical Synthesis: The solubility of FeCl3 in water and other solvents makes it a valuable precursor for the synthesis of various iron-containing compounds and materials.
- Analytical Chemistry: FeCl3 is used as a reagent in analytical chemistry techniques, such as colorimetric analysis, where its solubility allows for the formation of colored complexes with various analytes.
Understanding the solubility characteristics of FeCl3 is crucial for optimizing these and other applications, ensuring efficient and effective performance.
Conclusion
Ferric chloride (FeCl3) is a highly soluble compound in water, as indicated by its solubility rules and solubility charts. While the exact quantitative data on its solubility is not readily available, FeCl3 is known to be slightly soluble in water. By delving into the underlying principles, factors affecting solubility, and practical applications, this comprehensive guide provides a deep understanding of FeCl3 solubility, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate its scientific and industrial uses effectively.
References:
- Ferric Chloride Complexes in Aqueous Solution: An EXAFS Study, ResearchGate, 2018-05-05, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324973722_Ferric_Chloride_Complexes_in_Aqueous_Solution_An_EXAFS_Study
- Solubility relations in the ternary system NaCl-FeCl2-H2O, Science.gov, 1986-01-01, https://www.science.gov/topicpages/f/ferric%2Bchloride%2Bfecl3
- Is FeCl3 Soluble or Insoluble in Water? – YouTube, 2020-03-24, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KLW4Il_p0LI
- Ferric Chloride – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics, ScienceDirect, https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/ferric-chloride
- Ferric Chloride | FeCl3 | CID 24380 – PubChem, PubChem, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ferric-Chloride

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.