Prokaryotes are the one that lack a nucleus and also the rest of the organelles. They are mostly single celled and are small.
With the question for do prokaryotes have DNA replication, the answer is yes. Inside the prokaryotes there is just a single origination point where replication takes places in two paths and is always at same time. It takes place inside the cytoplasm.
The replication in DNA for the prokaryotes is the process where the organism do duplicate the DNA in a on other copy and is passed on to the daughter cells. It is usually generalized for E.Coli but is also shown by bacteria.
Replication of DNA is however a bi-directional one and generates at the one point for the purpose of replication. It also has there steps that includes the initiation, the elongation and the termination.
What is DNA replication in prokaryotes called and why?
The time when the prokaryotes do DNA replication, there is a theta like structure seen at the site of replication.
The process for DNA replication in the prokaryotes is called as Theta replication. The reason for this is that during the process it makes a resemblance of a Greek letter called theta (θ).
A theta structure is an intermediate structure that is formed during the process for replication of DNA that is circular. There is an unwinding if the helix that is double stranded and makes a loop which is called the replication bubble.
In the theta replication, the DNA which is double stranded unwinds itself at the site of replication that helps makes the stands for nucleotides helping them to serve as the templates which shall be the base for DNA synthesizing.
While the unwinding takes places there is a formation of loop and s called the replication bubble. The process for unwinding may take place in both the ends or in one side of bubble that makes it quite large. The process for DNA replication on both the strands goes equal with unwinding.
The point where there is unwinding, the pace where the strands for nucleotides gets separated from the circular DNA helix that is double stranded is termed as the replication fork.
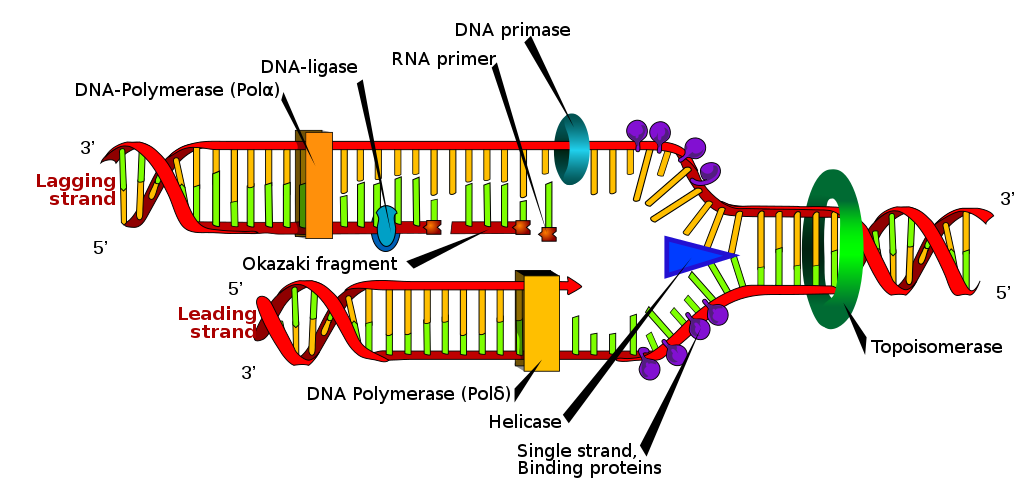
Where does DNA replication occur in prokaryote?
Inside the prokaryotes there is only one point for replication where the process takes place in two separate paths in the similar time. DNA replication takes place before binary fission.
The answer for do prokaryotes have DNA replication is yes and the process of DNA replication for these organism takes place inside the cytoplasm of the cell. The DNA replication is seen inside the nucleus of the cell.
The process for DNA replication occurs prior to that of cell division which helps in ensuring that both the cells do receive the same copy of the genetic substance from the parent. The division in animals have different time period of completion.
The division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes do have similarities and differences for the size and the molecules being complex. The cells of the prokaryotes are quite in the structure with only little DNA and no organelles or nucleus.
The replication for DNA can also take place in a test tube and thus this process can be called to be self-replication. The mechanism for the process of DNA replication inside a test tube is the same as the way in the eukaryotes and the prokaryotes and mitosis or meiosis in the eukaryotes.
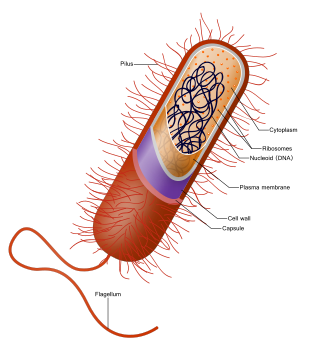
How do prokaryotes replicate?
The replication in DNA is so that there is a duplicate formation of the genetic material from the parent to the other getting passed to the daughter cells.
But on the other hand the reproduction process of the prokaryotes takes place via the process of cell division which is known as binary fission. It is just like the process of mitosis in the eukaryotes.
This procedure includes copying of the chromosomes an also separating of a single cell into two others. The process for binary fission is asexual mode of reproduction which involves no egg or sperm making.
There is no generation of sperm or egg or any type if mixing of the genetic material from the two organisms. There is an exception for a rare type of mutation or DNA sequence change, where the binary fission makes the daughter cells that are same to the mother cell.
The reproduction in prokaryotes is much faster than compared to the eukaryotes. The speed of division can be mentioned in regards to generation time or the time length from the making of one generation to the birth of the next one.
Well, with regards to do prokaryotes have DNA replication, not can all bacteria be quick in reproduction with some of that are pathogenic as well. Mycobacterium tuberculosis has a generation time for about 12 hours. They are still the fast multipliers in natural conditions and test tub in lab.
How do prokaryotes make DNA?
The reproduction in the prokaryotes is asexual and takes place generally by the binary fission, they have circular chromosome and do not go for mitosis.
The chromosome or the DNA of the prokaryotes is replicated and there are two copies as outcome which is different from each other for the reason being the mobility of the cell membrane to which they are adhered.
Prokaryotes are the organisms that often do lack any of the organelles and also the nucleus. But, they do have DNA which is circular and is stored in the central part of the call which is called the nucleoid that s in turn surrounded by the nuclear membrane.
The prokaryotes have a singular chromosome which is actually single and usually occupies a region of the cytoplasm and is called the nucleoid. They also include of many rigs that are small in size and are usually double stranded with having extra chromosome and are the plasmids.
A phenomenon in the prokaryotes is referred to as supercoiling that helps the organism in reducing the DNA and allows them for more space and so that the DNA can be kept packed easily. This is quite plectonemic as the chromosomes are actually small.
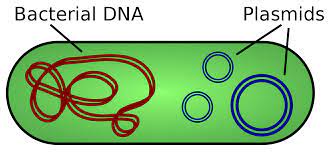
What are the characteristics of prokaryotic DNA replication?
The deoxyribonucleic acid and the chromosome in the prokaryotes is circular in shape with being located inside the cytoplasm of the cell.
The replication of the DNA in the prokaryotes is bi directional and generated from the single place of origin for replication. It takes place in the cytoplasm and occurs in the direction of 5’to 3’ direction.
The stands of the DNA are considered individually and are made in several directions that are to be followed. This gives them a lead and while generating of the lead it also makes a lagging strand.
The replication of DNA is actually a semiconservative process. It means that the each of the DNA stand is a double helix one and works as a template for getting a new one synthesized. This method takes it from one molecule to start with and then ending up for two daughter molecules.
The two new daughter molecules that are formed as a result are also double helix and have one old and one new strand carrying the copy of the genetic material from the parent. There is also formation of replication fork.
Why do prokaryotes only have one origin of replication?
In the prokaryotes, there are there vital types of polymerases that are called DNA pol I, DNA pol II, DNA pol III. These have only one site of replication origin.
The cell of the prokaryotes is much smaller and thus can get away with any process having only one site of origin. Mostly all the prokaryotes do have a single place of replication however the rate for the replication is also very high.
In the prokaryotes, the single place of replication does have many of the adenine and thiamine bases that have the hydrogen bonds on the weaker sides than compared to the guanine and cytosil pairs. It helps in making the DNA strands easier to separate.
There is an enzyme that is called the helicase that helps in unwinding of the DNA by getting the hydrogen bonds to break amongst all the nitrogenous base makings. With concern to this, eukaryotes and prokaryotes that different replication site.
What is unique about prokaryotic DNA replication?
There is only one point of replication of DNA for the prokaryotes which takes place in two directions and is concerned within the cytoplasm.
The uniqueness given by the prokaryotes are concerned with the replication site. The site of replication in length is approx. 245 bases in pairs in length and is quite in rich within Adenine and Thiamine.
The sequence of AT together is seen by some of the proteins that bind to the sites. There is an enzyme known as the helicase that helps in getting the DNA unwind itself with breaking of the hydrogen deals in the nitrogen pairs. The strands help in preventing the rewinding of the double helix.
After the DNA keeps on opening, the Y-shaped structures are called to be the replication forks. They are located in the site of replication and are usually bi directional as they proceed. There is also a single strand that binds the proteins which covers the single strands of DNA.
Another enzyme linked with it is the DNA polymerase II that adds up to the nucleotides taking each at a time on the DNA chain that is growing. The nucleotides that are added need energy, this energy is taken from the nucleotides that have phosphates linked with them and are three in number.
Is prokaryotic DNA replication unidirectional?
There is only one site for the part of replication for the concern in prokaryotes still the replication is rapid.
In regards with the prokaryotes the DNA replication process is nit unidirectional. They have only single site of origin for the purpose of replication and is bidirectional.
Bidirectional replication of the DNA is any mechanism that is ensured to all the eukaryotes and mostly all the prokaryotes cells. The replication that is unidirectional is rare and do is seen to take place only in very limited number of the cells of prokaryotes.
The reason for the DNA replication to be bidirectional is that the enzymes related to unwinding of the DNA called the DNA helicases cause the two of the parent DNA strands to get itself unwinded and then separates from one to the other in both ways at the same site that forms the Y-Shaped replication forks.
How many origins of replication do prokaryotes typically have?
The eukaryotes cells have DNA replication that is needed during the formation of replication forks with the prokaryotes being rapid.
There are three polymerases that has the single site for replication on the specific chromosome which is similar to many prokaryotes. It is approx. of length of 245 base pairs in length and is quite rich in AT pairs.
The cells for the prokaryotes uses up the single variety for the rapid replication propose. There are actually approx. about 350 origins of replication in the entire the genomes. On the contrary there is an estimation of 40,000 to 80,000 origins that get distributed via the human genome.
The replication in bacteria is regulated at the time of initiation stage. DNA is hydrolyzed into inactive by RIDA which is the regulator inactivation of the DnaA that gets converted to DnaA-ATP by the DARS. The complementary strand for 3’ to 5’ gets synthesized all time as the polymerase can add to nucleotides.
There are the three models that can be suggested for DNA replication. These are dispersive, conservative and semi-conservative. The method that is conservative suggest that the parental DNA and remains together and gets to form the parental DNA along with it together.
Is prokaryotic DNA replication conservative or semiconservative?
The genetic material needs to get itself replicated to get assure the policy for hereditary.
It has already been seen that DNA is replicated by the process which is semi conservative in the WT-4 cells that grow in 34 degrees Celsius or at the 38.5 degree covering the entire logarithmic phase and gets into the stationary phase.
The base system applied for the process of DNA replication is same from the microbes to the eukaryotes, there are a lot of variations that to make up the final product mode. The microbe DNA replication for some of the microbes do have ailments that are single stranded.
For this way, the replication of the genetic product shall be kept in consideration through the complementary strand inside the intermediate step for double stranded in the form of replication. All the form of DNA does need a region for replication to get the strands separated.
A very general and common character for the origins responsible for the separation of strands in the semiconservative replication process is that they are much rich in the A=T. Not so common about it is the prevalence of the G over the C and the T over the A in the prokaryotes which is also the leading strand.
Why is DNA replication faster in prokaryotes than eukaryotes?
The process of replication is much fast in prokaryotes than the other. Some of the bacteria take 40minies while animals cell take 400 hours.
The DNA polymerase is much rapid in regards to the base that is replicated per second; however it does have only one origin of replication. Eukaryotes have distinct way for replication.
On the other hand there are many site for replication in the eukaryotes, there are many parallel running DNA polymerases that make up the process of DNA replication easy and much faster in the eukaryotes.
The reason for the eukaryotes having many sites for working out the way from DNA replication is that they are much larger in size than the prokaryotes and also there are multiple functions being performed by them which mostly cover mobility.
Is prokaryotic DNA replication semi discontinuous?
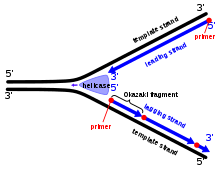
The experiments show that DNA replication is semi discontinuous on the lagging strand while leading has to be continuous.
The process for DNA replication is semi discontinuous as for one among the strands that is synthesized on regular basis and on the other hand another reason is for the formation of the Okazaki fragments which is formed discontinuously.
Semi discontinuous process is the double helix of the DNA that unwinds taking the replication on the 3’ to 5’ stand which gets to process itself easy in the 5’ to 3’. Here the leading strand is worked on continuous and the lagging one is taken for being discontinuous.
The process of replicating DNA in the prokaryotes is semi discontinuous. In some of the microbe, both of the stands can be made to copy on the 5’ to 3’ way together with no need for discontinuous process of replication.
How do you tell if a DNA sequence is prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
The prokaryotic cell do have only one strands of DNA that is circular while eukaryotes have maay linear type DNA.
The gene expression for the prokaryotes do take place in the cytoplasm for there is no definite nucleus and thus the DNA is free in the cytoplasm while the one in eukaryotes take places in the cytoplasm and nucleus.
The DNA that the prokaryotes have is in size small and is circular which is located in the cytoplasm. They are chromosomally arranged and are situated in the cell’s nucleus. The eukaryotic cell is more dense and complex and has organelle having membranes like the nucleus.
Unlike the DNA that is circular in the prokaryotic cells, it in general has only one site for getting the DNA replicated and in the eukaryotes there is a liners DNA in the eukaryotes cell that has many site for the replacing.
FAQs-
What is Replication fork?
The replication fork is formed inside the DNA within its long helical during the process of DNA replication. It is made up of helicases.
This helps in breaking of the hydrogen bonds that holds the stands of the DNA together inside the helix itself. The structure formed as a outcome has two of the prongs branched with each made up of the DNA that is single strand.
Do eukaryotes also have single replication site?
The chromosomes for the eukaryotes have multiple origin sites while just prokaryotes have only one.
This is so as the eukaryotic chromosome are bigger and having multiple origins saves them time. The eukaryotes stores the DNA in chromosomes of nucleus.
Without having many replication sites, the process for replication would take long; it would slow down the cell growth part and also cause degradation of quite few cells.
What is complementary strand?
They are either of the any two chains that do catch up with the double helix of the DNA with regards to the two chains that have been made from the complementary base pairs.
Also Read:
- Antiparallel dna strands 2
- Dna transcription enzyme
- Is prokaryotic dna a double helix
- Dna transcription diagram
- Sequence of nitrogenous bases in dna
- Uracil in dna replication
- Dna replication vs polymerase
- Chromatin organization impact on packaging of dna
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.