Cl2O6 or chloryl perchlorate is the dimer of chlorine trioxide having a molecular weight of 166.901 g/mol. Let us explore the molecular property of Cl2O6 in detail.
Chlorine trioxide is an odd electron system so it is not stable as per octet because the octet is incomplete and there is electron deficiency present over the Cl center. Then two ClO3 centers come close together to form Cl2O6 via the Cl-Cl bond. It is another example of a 3e-4c system around both Cl centers.
There is steric repulsion occured between the Cl-Cl bond and the lone pairs repulsion. Now we explain the hybridization, lewis structure, polarity, and other molecular property of the Cl2O6 with proper explanation in the next part.
1. How to draw Cl2O6 structure?
The lewis structure of the Cl2O6 can give us an idea of the different molecular properties of the molecule. Let us try to draw the lewis structure of Cl2O6 in a few steps.
Counting the valence electrons
1st step of drawing a lewis structure of a molecule is counting its total valence electrons, and while counting total valence electrons just count the valence electrons of the substituent atoms and add them together. The total valence electrons counted to be 50 for the Cl2O6 for two Cl and six O atoms.
Choosing the central atom
For drawing the lewis structure we need to choose a central atom and based on the central atoms surrounding atoms are placed accordingly. Based on size and electronegativity, Cl is chosen as the central atom here. Both the Cl atoms are the central atoms and six O atoms are surrounding atoms.
Satisfying the octet
Every p block element follows octet after bond formation by completing their valence orbital by eight numbers of electrons. Cl and O both are p block elements so, they need eight electrons in their valence orbital. So, they share electrons during the bond formation and the electrons are needed 8*8 = 64.
Satisfying the valency
During the satisfaction of their octet, every atom should compatible with their valency. The stable valency of O is 2 and for Cl is 7. the remaining electrons 64-50 = 14 should be accompanied by their stable valency. Each Cl forms seven bonds and each O make double bonds to fulfill their valency.
Assign the lone pairs
After the bond formation excess, nonbonded electrons exist as lone pairs over the respective atoms. O has lone pairs after the double bond formation because it has four more electrons in its valence shell but all the seven electrons of the Cl are being used in the bond formation. So, it is a lack of lone pairs.
2. Cl2O6 valence electrons
The electrons present in the valence shell and involved in the bond formation of every atom are called valence electrons. Let us count the total valence electrons for Cl2O6.
The total valence electrons for the Cl2O6 molecule are 50, which is the contribution of the Cl and O atoms. Valence electrons for a molecule are the summation of valence electrons of the individual atoms present in it. The valence electrons for Cl and O are confirmed from their position in the periodic table.
- The valence electrons for the Cl atoms are 7 (as it is a group VIA element)
- The valence electrons for the O atoms are 6 (as it is a group VIA element)
- So, the total valence electrons present in the Cl2O6 are 7*2 + 6*6 = 50
3. Cl2O6 structure lone pairs
The remaining electrons in the valence orbital after bond formation is known as lone pairs. Let us count the lone pairs of the Cl2O6 molecule.
The total lone pairs present over the Cl2O6 molecule are 12 pairs which mean 24 lone pairs of electrons. The numbers are only from the O because Cl atoms are involved in all the valence electrons in the bond formation. But O has extra four electrons in the outermost orbital which exist as lone pairs.
- formula for calculating the lone pairs over Cl2O6 , non-bonded electrons = valence electrons – bonded electrons
- The lone pairs present over each Cl atom are 7-7= 0
- The lone pairs present over each O atom are 6-2= 4
- So, the total number of lone pairs present over the Cl2O6 molecule is 4*3 =12 pairs which means 24 lone pairs electrons.
4. Cl2O6 structure shape
The molecular shape is formed by the proper arrangement of the central and other substituent atoms to avoid repulsion. Let us predict the shape of Cl2O6.
The molecular shape is tetrahedral making each Cl and three O atoms which is confirmed by the following table.
| Molecular Formula | No. of bond pairs | No. of lone pairs | Shape | Geometry |
| AX | 1 | 0 | Linear | Linear |
| AX2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | Linear |
| AXE | 1 | 1 | Linear | Linear |
| AX3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | Trigonal Planar |
| AX2E | 2 | 1 | Bent | Trigonal Planar |
| AXE2 | 1 | 2 | Linear | Trigonal Planar |
| AX4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral |
| AX3E | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | Tetrahedral |
| AX2E2 | 2 | 2 | Bent | Tetrahedral |
| AXE3 | 1 | 3 | Linear | Tetrahedral |
| AX5 | 5 | 0 | trigonal bipyramidal | trigonal bipyramidal |
| AX4E | 4 | 1 | seesaw | trigonal bipyramidal |
| AX3E2 | 3 | 2 | t-shaped | trigonal bipyramidal |
| AX2E3 | 2 | 3 | linear | trigonal bipyramidal |
| AX6 | 6 | 0 | octahedral | octahedral |
| AX5E | 5 | 1 | square pyramidal | octahedral |
| AX4E2 | 4 | 2 | square pyramidal | octahedral |
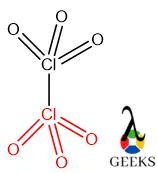
So, from the above table, it is confirmed that Cl2O6 is an AX3 type of molecule around each central atom. So, according to the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electrons Pair Repulsion) theory, the AX3 type of molecule adopted tetrahedral geometry around the central atom., because there are no lone pairs over the central atom.
5. Cl2O6 structure angle
For a particular shape of molecule then there will be a particular bond angle present for proper orientation of the atoms. Let us calculate the bond angle for Cl2O6.
The particular bond angle for the tetrahedral molecule is 109.50 which can be calculated by the VSEPR theory or hybridization value. When a tetra-coordinated molecule arranged in a tetrahedral geometry then there will be steric repulsion occur and for this reason, all atoms are made at that particular angle.
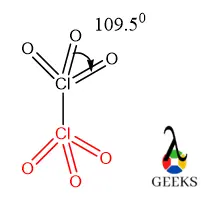
We can calculate the bond angle theoretically by the hybridization value of the central atom.
- By the bent’s rule, we can calculate the bond angle using the formula COSθ = s/(s-1).
- The central atom Cl is sp3 hybridized, so the s character here is ¼th
- So, the bond angle is, COSθ = {(1/4)} / {(1/4)-1} =-( 1/3)
- Θ = COS-1(-1/3) = 109.470
- There is no deviation factor present so the bond angle is perfectly 109.50.
6. Cl2O6 hybridization
Mixing of two or more atomic orbitals undergoing hybridization form an equal number of hybrid orbital of equivalent energy. Let us know the hybridization of Cl2O6.
Each Cl in the Cl2O6 molecule is sp3 hybridized, which can be shown in the following table.
| Structure | Hybridization value | State of hybridization of central atom | Bond angle |
| 1.Linear | 2 | sp /sd / pd | 1800 |
| 2.Planner trigonal | 3 | sp2 | 1200 |
| 3.Tetrahedral | 4 | sd3/ sp3 | 109.50 |
| 4.Trigonal bipyramidal | 5 | sp3d/dsp3 | 900 (axial), 1200(equatorial) |
| 5.Octahedral | 6 | sp3d2/ d2sp3 | 900 |
| 6.Pentagonal bipyramidal | 7 | sp3d3/d3sp3 | 900,720 |
- We can calculate the hybridization by the convention formula, H = 0.5(V+M-C+A),
- So, the hybridization of central Cl is, ½(7+1+0+0) = 4 (sp3)
- One s orbital and three p orbitals of each Cl are involved in the hybridization.
- The lone pairs of O are not involved in the hybridization.
7. Is Cl2O6 solid or gas?
The physical state of every molecule depends on the temperature and also constituents present within it. Let us check whether Cl2O6 is solid or gas.
Cl2O6 is neither solid nor gas it is liquid at room temperature. The bond between two Cl atoms are exist the atoms close to each other and therefore the van der Waal’s force of attraction increases. But not so high that it can exist as a solid state at room temperature. The density increased for the dimer.
8. Is Cl2O6 soluble in water?
The solubility in water depends on the ability to make H-bonding of atoms and dissolved in the aqueous solution. Let us see whether Cl2O6 is soluble in water or not.
Cl2O6 is not soluble in water actually it reacts with a water molecule. The Cl-Cl bond is very weak as both are electronegative atoms and draw electron density toward themselves. So, water molecules can easily break the bond and are prone to nucleophilic attacks. So, it’s difficult to say soluble in water.
9. Is Cl2O6 a molecular compound?
When a molecule is formed by maintaining the stable valency of substituent atoms known as a molecular compound. Let us see whether Cl2O6 is a molecular compound or not.
Cl2O6 is a molecular compound because the valence of Cl and O are fully satisfied here. The stable valency of O is 2 and each O forms a double bond with the Cl atom, again the stable valency of Cl is 7, and the heptavalency of Cl is maintained here. Also, there is a ratio stoichiometric is fixed.
The ratio of monomer is always 1:3 and for also dimer is 1:3 as there are two Cl atoms and six O atoms present.
10. Is Cl2O6 acid or base?
In the aqueous solution if a substance release H+ or OH– then it is called acid or base respectively – Arrhenius theory. Let us see whether Cl2O6 is acid or base.
Cl2O6 is neither acid nor base rather it is an acidic oxide. Because it cannot fulfill the Arrhenius theory because it lacks those ions, again, it cannot accept electrons because there is no free space available in the molecule and also due to electronegativity it cannot release electrons easily.
Being an acidic oxide when it reacts with water it can form acid but not behave like acid itself. Non-metal oxides are acidic oxides.
11. Is Cl2O6 electrolyte?
Electrolytes are that substance who can dissociate from an aqueous ion and carry the electricity through the solution. Let us see whether Cl2O6 is an electrolyte or not.
Cl2O6 can behave as an electrolyte because it can be dissociated [ClO2]+ and [ClO4]– in the aqueous solution. Both radicals are highly charged particles because in both electronegative Cl atoms are present. So, both radicals make the solution charged and for this reason, can carry electricity easily.
12. Is Cl2O6 salt?
Salt is formed by a cation other than H+ and anion other than OH– and bonded with ionic interaction. Let us check whether C2O6 is salt or not.
Cl2O6 is not salt as it is an acidic oxide. Although it has a cation and anion other than H+ and OH– but the bond present between atoms are purely covalent bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between O and Cl atoms. So, it cannot be salt anymore but it can be dissociated and carried electricity.
13. Is Cl2O6 polar or nonpolar?
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of a permanent resultant dipole-moment value by the shape. Let us check whether Cl2O6 is polar or not.
Cl2O6 is a non-polar molecule because there is zero dipole-moment value present. Although the molecule is asymmetrical around the monomeric form in dimer the dipole-moment from O to Cl is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. So, cancel out each other and makes the dipole-moment value zero.
14. Is Cl2O6 ionic or covalent?
According to Fajan’s rule, no molecule has 100% ionic or covalent character, they are just vice versa basis of the polarizability rule. Let us see if Cl2O6 is ionic or covalent.
Cl2O6 is a pure covalent molecule because the bond present between Cl and O and even Cl and Cl are made by the sharing of electrons by both atoms equally. Again, the polarizing power of the Cl is very low because it has a lower ionic potential value, and again oxide has poor polarizability as it is lower in size.
Cl2O6 has more covalent character than its ionic nature although some of the ionic nature is reflected in chemical reactions.
Conclusion
The dimer is more susceptible to nucleophilic attack because the bond present between two Cl atoms is very weak in nature and easily be cleaved by the attack of any external nucleophile. To remove the electron deficiency monomer forms the dimeric form of the molecule.

Hi……I am Biswarup Chandra Dey, I have completed my Master’s in Chemistry from the Central University of Punjab. My area of specialization is Inorganic Chemistry. Chemistry is not all about reading line by line and memorizing, it is a concept to understand in an easy way and here I am sharing with you the concept about chemistry which I learn because knowledge is worth to share it.