Chloromethane is an organic compound. Let us discuss some interesting facts about chloromethane.
Chloromethane belongs to organohalogens and is abundantly found in nature. It can also be synthesized in laboratories or industries. Chloromethane can be used as a reagent in many reactions and is mostly used as a methylating agent.
In this article, we will study some of the important properties of chloromethane like chemical formula, viscosity, melting and boiling point, and some reactions.
Chloromethane IUPAC name
The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) name of chloromethane is chloromethane. It is commonly known as methyl chloride.
Chloromethane chemical formula
The chemical formula of chloromethane is CH3Cl. It contains one carbon atom, three hydrogen atoms, and one chlorine atom. The chlorine and hydrogen atoms are directly attached to the carbon atom.
Chloromethane CAS number
The CAS number (authentic numeric identifier which can contain upto10 digits) of chloromethane is 74-87-3.
Chloromethane ChemSpider ID
The ChemSpider ID (ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database) of chloromethane is 6087.
Chloromethane chemical classification
Chloromethane comes under the category of haloalkanes, where the chlorine atom is attached to the carbon atom via a single bond.
Chloromethane molar mass
The molar mass of chloromethane is 50.49 g/mol.
Chloromethane color
Chloromethane is a colorless gas.
Chloromethane viscosity
The viscosity of chloromethane is different at different temperatures.
| Temperature | Viscosity |
|---|---|
| 0 °C | 0.2280 mPa.s |
| 20 °C | 0.1784 mPa.s |
| 40 °C | 0.1440 mPa.s |
Chloromethane molar density
In the gaseous state, at 0 °C, the molar density of chloromethane is 0.0457 mol/cm3, as the density is 2.3065 g/cm3. In the liquid state, at -23.8 °C, the molar density of chloromethane is 0.0199 mol/cm3, as the density is 1.003 g/cm3.
Chloromethane melting point
The melting point of chloromethane is -97.4 °C (175.8 K) or -143.3 °F.
Chloromethane boiling point
The boiling point of chloromethane is -23.8 °C (249.3 K) or -10.8 °F.
Chloromethane state at room temperature
At room temperature, chloromethane is gas but under pressure it becomes liquid.
Chloromethane covalent bond
Chloromethane contains four covalent bonds. The carbon present in chloromethane, has a valency of four. The three valence electrons are shared with three hydrogen atoms forming three covalent bonds and the remaining one with chlorine forming one covalent bond.

Chloromethane covalent radius
The covalent radius of chloromethane cannot be determined as the covalent radius of compounds cannot be determined.
Chloromethane electron configurations
Electron configuration shows the arrangement of electrons in an orbital around the nucleus of an atom. Let us discuss the electronic configuration of chloromethane in detail.
The electronic configuration of carbon is shown as [He] 2s2 2p2, hydrogen is 1s1 and that of chlorine is [Ne] 3s2 3p5.
Chloromethane oxidation state
The oxidation state of carbon in chloromethane is -2. Each of the three hydrogen atoms is in a +1 oxidation state and the chlorine atom is in a -1 oxidation state.
Chloromethane acidity
Chloromethane is acidic in nature. On hydrolysis, it gives methanol and hydrochloric acid.

Is chloromethane odourless
Chloromethane is mainly odourless.
Is chloromethane paramagnetic
A paramagnetic substance contains unpaired electron(s) and shows low positive susceptibility. Lets us discuss about the paramagnetic behavior of chloromethane.
Chloromethane is not paramagnetic as the magnetic susceptibility is -32.0×10-6 cm3/mol and it is a negative value.
Chloromethane hydrates
Chloromethane exists as a hydrate where two molecules of chloromethane and one molecule of water are present. The molecular formula is C2H8Cl2O.
Chloromethane crystal structure
It is difficult to predict the crystal structure of chloromethane. By X-ray diffraction at an angle of -125°, it is predicted that the carbon-chlorine bond distance is 1.805 Å.
Chloromethane polarity and conductivity
- Chloromethane is a polar compound. Because of the C‒Cl bond there exists a net dipole and hence making chloromethane a polar compound.
- Chloromethane is a poor conductor as the degree of dissociation is very low.
Chloromethane reaction with acid
Chloromethane does not react with acids.
Chloromethane reaction with base
Chloromethane reacts with a base. For example, chloromethane reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to give methanol (CH3OH) and sodium chloride (NaCl).

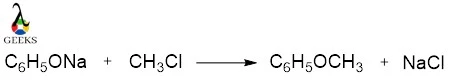
Chloromethane reaction with oxide
Chloromethane reacts with oxides. For example, chloromethane reacts with sodium phenoxide to give methyl phenyl ether, this reaction is known as Williamson ether synthesis.
Chloromethane reaction with metal
Chloromethane reacts vigorously with metals like sodium, potassium, magnesium, zinc, etc. For example, methyl chloride reacts with sodium to give ethane, this reaction is known as Wurtz reaction.

Conclusion
Chloromethane is an anthropogenic and flammable gas. It is formerly used as a refrigerants and very less commonly used in consumer products. Chloromethane is also used in the extraction of resins, greases, in the making of methylcellulose.

Hello! I am Debashruti Bandyopadhyay. I have completed my Ph.D. in Chemistry from NISER Bhubaneswar. My area of research is synthetic organic chemistry. I have worked as a student coordinator and SME for a startup for 5 months. Presently, I am working as a Subject Matter Expert in LambdaGeeks.