Carbon Tetraiodide Properties (25 Facts You Should Know)
Carbon tetraiodide is an organic compound that is also known as tetrahalomethane. Let us learn some facts like the physical state, appearance, and chemical features of carbon tetraiodide.
The molecular geometry of Carbon Tetraiodide is tetrahedral. Carbon tetraiodide is thermally unstable due to its greater atomic size and it has zero dipole moment due to its symmetrical structure.
Let us focus on a few properties like molar mass, oxidation state, magnetic character, etc. with detailed explanations.
Carbon Tetraiodide IUPAC Name
The IUPAC name (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) of carbon tetraiodide is Tetra iodomethane.
Carbon Tetraiodide Chemical Formula
Carbon tetraiodide has the chemical formula CI4. Here the central Carbon atom is surrounded by four different Iodine atoms. The type of bond that exists between four C-I is a single bond.
Carbon Tetraiodide CAS Number
Carbon tetraiodide has the CAS registry number (authentic numeric identifier which can contain upto10 digits) 507-25-5.
Carbon Tetraiodide ChemSpider ID
Sulfuric acid has the ChemSpider ID (ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database) 10055.
Carbon Tetraiodide Chemical Classification
Carbon tetraiodide can be chemically classified as a Crystalline solid compound with tetragonal geometry.
Carbon Tetraiodide Molar Mass
The molar mass of carbon tetraiodide is 519.6286 g/mol.
Carbon Tetraiodide Color
Carbon tetraiodide is a dark violet crystalline solid.
Carbon Tetraiodide Molar Density
The molar density of carbon tetraiodide is 0.00831 mol/cm3 because it has a density of 4.32 g/cm3. To find out the molar density we need to divide the molar mass of the given substance by its density.
Carbon Tetraiodide Melting Point
Carbon tetraiodide has a melting point of 1710 C or 339.80 F.
Carbon Tetraiodide Boiling Point
The boiling point of carbon tetraiodide is 329.20 C or 624.560 F.
Carbon Tetraiodide state at Room Temperature
At room temperature, carbon tetraiodide exists in the solid state. It is a crystal powder at 20oC.
Carbon Tetraiodide Covalent Bond
In carbon Tetraiodide, four covalent bonds are formed between carbon and Iodine atoms. Carbon & Iodide both are non-metals. Therefore, the bond that exists between C-I is covalent and CI4 is a covalent compound.
Carbon Tetraiodide Covalent Radius
The covalent radius of Carbon tetraiodide i.e a C-I bond length of 215.4 pm.
Carbon Tetraiodide Electron Configurations
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in different atomic orbitals in any atom. Let us learn about the electron configuration of Carbon & Iodine-atoms of CI4 in detail.
The electronic configuration of C with atomic number 6 is [He] 2s2 2p2 and Iodine with an atomic number 53 is [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 respectively. The electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s1. Each atom has a different notation to depict its electronic structure.
Carbon Tetraiodide Oxidation State
The central atom, carbon is in a +4-oxidation state in carbon tetraiodide. All the halogens have a -1-oxidation state. Iodine belongs to the halogen family thus its oxidation state is -1.
Carbon Tetraiodide acidity/alkaline
Carbon Tetraiodide is neither acidic nor alkaline due is poor solubility in water and it has no effect on solution pH.
Is Carbon Tetraiodide odourless?
Carbon tetraiodide is not an odourless solid. It has an order of iodine as it contains four iodine atoms.
Is Carbon Tetraiodide Paramagnetic?
If some materials are weakly attracted by magnets due to the presence of unpaired electrons then it is known as paramagnetic. Let us see the magnetic nature of carbon Tetraiodide.
Carbon tetraiodide is not a paramagnetic compound. It is a diamagnetic substance due to the presence of no unpaired electrons.
Carbon Tetraiodide Hydrates
The crystal of carbon tetraiodide do not form hydrates because it is insoluble in water.
Carbon Tetraiodide Crystal Structure
Solid Carbon tetraiodide possesses a Tetragonal crystal structure. The space group of the Carbon tetraiodide crystal in a cell with the dimensions a= 6.409, c= 9.558.
Carbon Tetraiodide Polarity and Conductivity
- Carbon Tetraiodide forms a non-polar covalent bond due to which it is insoluble in water.
- CI4 cannot conduct electricity as all the electrons are mutually shared with no availability of free ions.
Carbon Tetraiodide Reaction with Acid
Carbon Tetraiodide reacts with a strong acid like SbF5 in presence of solvent SO2ClF to yield corresponding tri-iodomethyle carbonium ions.
CI4 + SbF5 = [CI3]+ + [SbIF5]–
Carbon Tetraiodide Reaction with Base
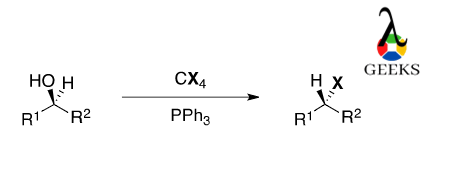
Carbon Tetraiodide generates alkyl iodide from alcohol. The reaction proceeds with triphenylphosphine in presence of base-like secondary alcohol and converts ketones into alkyl iodide. This reaction is also known as the Apple reaction.
Carbon Tetraiodide Reaction with oxide
Carbon Tetraiodide does not react with oxides due to an increase in nucleophilicity of Iodine and decreases in electronegativity due to the greater atomic size of I.
Carbon Tetraiodide Reaction with Metal
Carbon Tetraiodide does not react with metals as it is thermally unstable.
Conclusion
Carbon Tetraiodide is a source of iodine and considers a toxic substance. It is used as an iodination reagent. It is a methane derivative and contains 2.3% weight of carbon.

Hello Everyone, I am Arunima Chakraborty. I have completed my MPhil in Chemistry from Christ University, Bangalore. I have 5.8 years of experience in curriculum designing & teaching. Currently, I am working as an SME with Lambda Geeks. Let’s connect through LinkedIn:https://www.linkedin.com/in/arunima-chakraborty-87192a156