The boiling point of sulfuric acid, a crucial physical property, is influenced by its concentration and the presence of other substances, such as water. Understanding the intricacies of this parameter is essential for various scientific and industrial applications.
Understanding the Boiling Point of Pure Sulfuric Acid
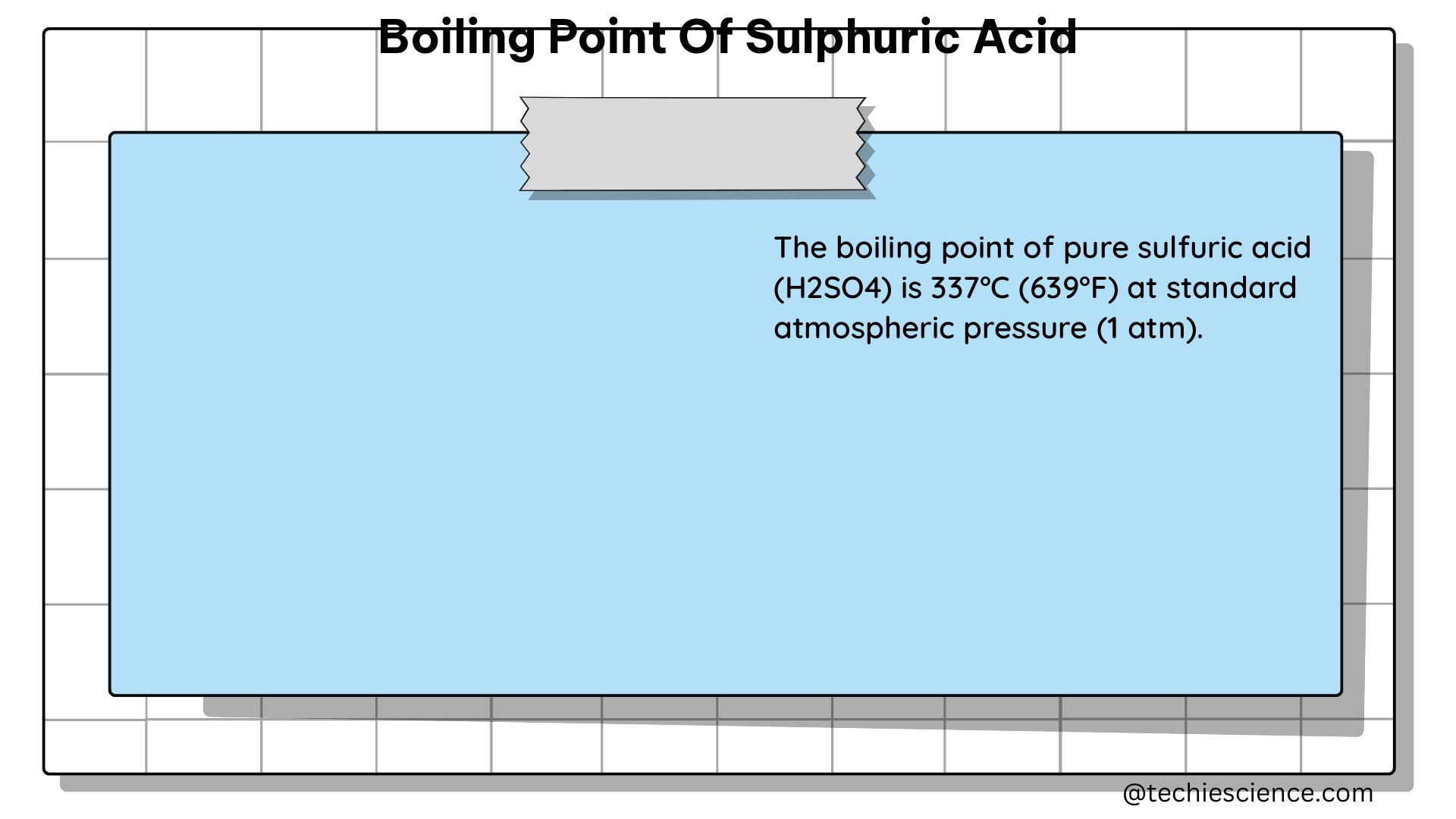
Pure sulfuric acid (H2SO4) has a boiling point of approximately 337°C (639°F) at standard atmospheric pressure (101.3 kilopascals or 1 atmosphere). This high boiling point is attributed to the strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the sulfuric acid molecules, which requires a significant amount of energy to overcome.
The boiling point of sulfuric acid can be expressed using the following formula:
Tb = Tb,0 + Kb * m
Where:
– Tb is the boiling point of the solution (in °C)
– Tb,0 is the boiling point of the pure solvent (in this case, water at 100°C)
– Kb is the boiling point elevation constant for sulfuric acid (3.84°C/m)
– m is the molality of the sulfuric acid solution (in mol/kg)
This formula demonstrates the relationship between the boiling point of the solution and the concentration of sulfuric acid, as the boiling point increases with increasing acid concentration.
Boiling Point of Sulfuric Acid-Water Mixtures
The boiling point of sulfuric acid-water mixtures can vary significantly depending on the concentration of sulfuric acid. As the concentration of sulfuric acid increases, the boiling point of the mixture also increases, due to the higher boiling point of sulfuric acid compared to water.
Here are some examples of the boiling points of sulfuric acid-water mixtures at different concentrations:
| Sulfuric Acid Concentration (% v/v) | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|
| 10% | 103.9 |
| 25% | 109.2 |
| 50% | 156.4 |
| 75% | 235.8 |
| 90% | 290.9 |
| 98% | 337.0 |
These values illustrate the significant impact of sulfuric acid concentration on the boiling point of the solution. As the concentration increases, the boiling point rises dramatically, reaching the maximum of 337°C for pure sulfuric acid.
Factors Affecting the Boiling Point of Sulfuric Acid
Several factors can influence the boiling point of sulfuric acid, including:
-
Concentration: As mentioned earlier, the concentration of sulfuric acid in the solution is the primary factor affecting the boiling point. Higher concentrations lead to higher boiling points.
-
Pressure: The boiling point of sulfuric acid, like any other substance, is affected by the surrounding pressure. Increasing the pressure will raise the boiling point, while decreasing the pressure will lower it.
-
Presence of Impurities: The presence of impurities, such as other dissolved substances, can alter the boiling point of the sulfuric acid solution. Impurities can either increase or decrease the boiling point, depending on their nature and concentration.
-
Molecular Interactions: The strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding between sulfuric acid molecules is a significant factor contributing to the high boiling point of the pure substance. The disruption or strengthening of these interactions can affect the boiling point.
-
Solvation Effects: The interaction between sulfuric acid and the solvent (e.g., water) can also influence the boiling point. The solvation of sulfuric acid molecules can alter the overall solution properties, including the boiling point.
Applications of Sulfuric Acid Boiling Point Knowledge
The understanding of the boiling point of sulfuric acid and its variations with concentration has several practical applications:
-
Preparation of Dilute Sulfuric Acid Solutions: The boiling point data is used to prepare more dilute sulfuric acid solutions from concentrated “constant boiling” sulfuric acid, which has a fixed composition and boiling point.
-
Industrial Processes: The boiling point information is crucial in various industrial processes, such as the production of fertilizers, the manufacture of other chemicals, and the treatment of metal surfaces.
-
Safety Considerations: Knowing the boiling point of sulfuric acid is essential for handling and storing the substance safely, as it can help identify potential hazards and implement appropriate safety measures.
-
Thermodynamic Modeling: The boiling point data of sulfuric acid-water mixtures is used in thermodynamic models and simulations to predict the behavior of these systems in various applications.
-
Analytical Chemistry: The boiling point of sulfuric acid solutions is a valuable parameter in analytical chemistry, where it can be used for identification, purity determination, and other analytical purposes.
Conclusion
The boiling point of sulfuric acid is a critical physical property that is influenced by various factors, including concentration, pressure, and the presence of impurities. Understanding the intricacies of this parameter is essential for a wide range of scientific and industrial applications, from the preparation of dilute acid solutions to the safe handling and storage of this highly corrosive substance. By mastering the knowledge of sulfuric acid boiling points, researchers, chemists, and engineers can optimize their processes, ensure safety, and advance their respective fields.
References:
- Properties of Sulphuric Acid/Water Mixtures as Solvents. In: Chemical Reviews. 1983.
- Sulfuric acid 25% (v/v) in aqueous solution (1 + 3). In: VWR.
- Boiling sulfuric acid. In: WorldWideScience.org.
- Thermodynamic Properties of Aqueous Sulfuric Acid. In: Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 2014.

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.