The boiling point of ethanoic acid, also known as acetic acid, is a crucial property that has been extensively studied and documented. This compound, with the chemical formula CH3COOH, is a widely used organic acid with a wide range of applications in various industries, from food preservation to chemical synthesis.
Understanding the Boiling Point of Ethanoic Acid
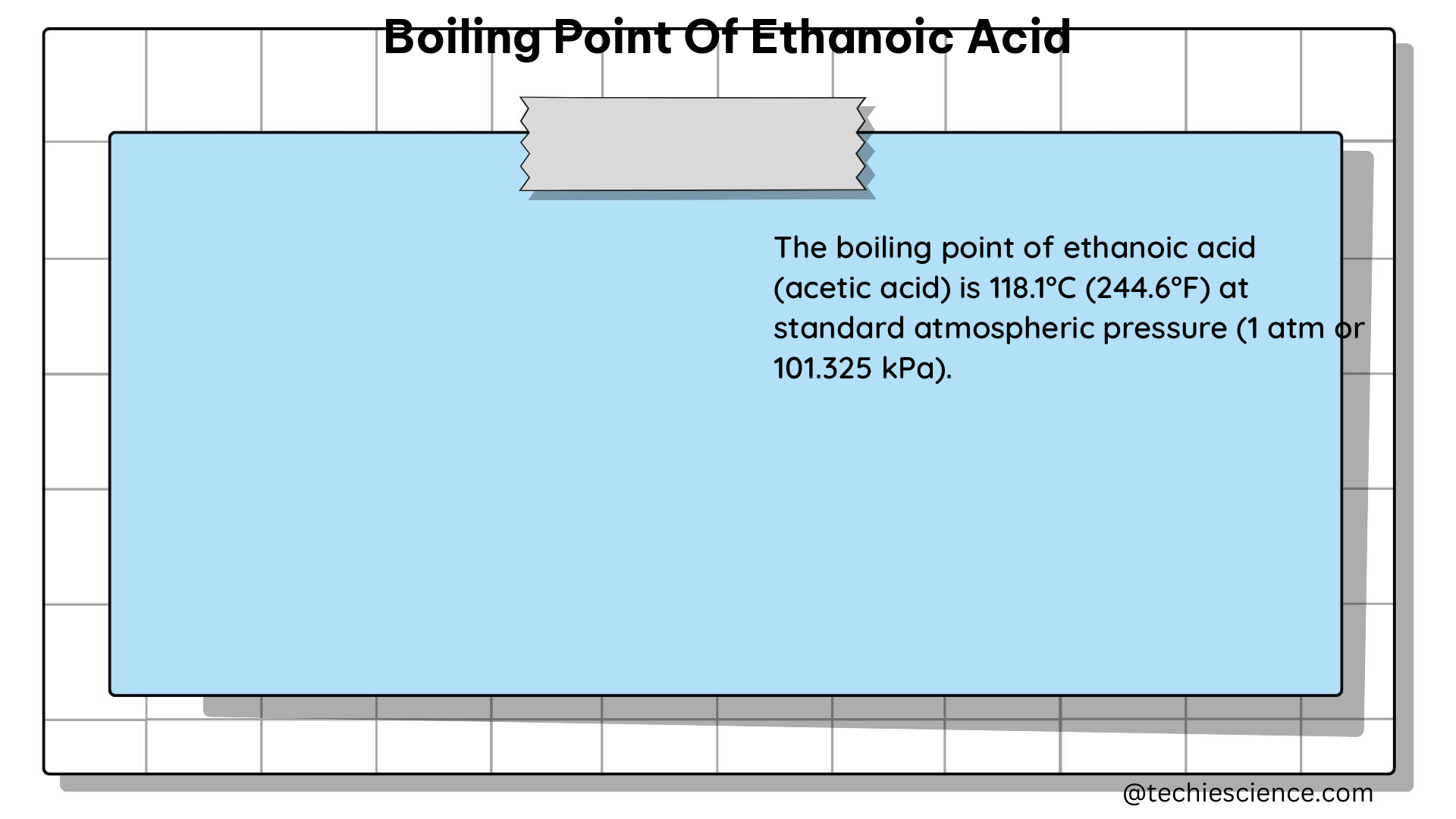
The boiling point of ethanoic acid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure, causing the liquid to transition into a gaseous state. According to multiple sources, the boiling point of ethanoic acid is approximately 117.9 degrees Celsius or 244.2 degrees Fahrenheit.
This temperature is influenced by several factors, including the presence of solutes, temperature, intermolecular forces, and the polarity of the solvent. Understanding these factors is essential for effectively utilizing and manipulating the boiling point of ethanoic acid in various applications.
Factors Affecting the Boiling Point
-
Presence of Solutes: Adding ethanoic acid to water or other liquids can lower the boiling point due to the decrease in vapor pressure caused by the solute-solvent interactions.
-
Temperature: Increasing the temperature of ethanoic acid can raise its boiling point due to the increase in vapor pressure.
-
Intermolecular Forces: Ethanoic acid has relatively weak intermolecular forces, which contributes to its relatively low boiling point compared to other chemicals. However, adding compounds with stronger intermolecular forces, such as water, can raise the boiling point of ethanoic acid.
-
Polarity of the Solvent: In general, more polar solvents have a lower boiling point than less polar solvents. Ethanoic acid only boils at 118.1 degrees Celsius in non-polar solvents, such as cyclohexane, hexanes, and carbon tetrachloride. However, in polar solvents like ethanol and acetone, ethanoic acid boils at a much lower temperature, around 90 degrees Celsius, due to the hydrogen bonding between the solvent and ethanoic acid molecules.
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications for the boiling point of ethanoic acid can vary depending on the specific application or industry. However, some general specifications include:
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point Range | 117.9 – 118.1 degrees Celsius (244.2 – 244.6 degrees Fahrenheit) |
| Vapor Pressure at Boiling Point | 101.3 kPa (1 atm) |
| Intermolecular Forces | Dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces |
| Solubility in Water | Miscible |
| Polarity | Polar |
| Molecular Weight | 60.05 g/mol |
These specifications can be useful for determining the suitability of ethanoic acid for various applications, such as chemical reactions, solvent extraction, or distillation processes. They can also help to ensure consistent quality and performance in industrial or laboratory settings.
Measuring the Boiling Point of Ethanoic Acid
To measure the boiling point of ethanoic acid at home, you can follow these steps:
- Obtain a sample of pure ethanoic acid from a reputable source.
- Clean and dry a glass boiling tube or other appropriate container.
- Measure out a small amount of ethanoic acid (e.g., 30 cm3) using a graduated cylinder or pipette.
- Carefully pour the ethanoic acid into the boiling tube, taking care not to spill or contaminate the sample.
- Heat the boiling tube gently over a Bunsen burner or other heat source, monitoring the temperature carefully with a thermometer.
- Record the temperature at which the ethanoic acid begins to boil and vaporize.
- Repeat the experiment several times to ensure accuracy and consistency.
By following these steps, you can measure the boiling point of ethanoic acid with relative ease and accuracy, and gain a better understanding of this important chemical property.
Unique Perspectives
One unique perspective to consider when discussing the boiling point of ethanoic acid is its relationship to the boiling points of other chemicals. For example, ethanoic acid has a higher boiling point than ethanol (78 degrees Celsius) and ethanal (21 degrees Celsius), indicating that it has stronger intermolecular forces and is less volatile than these chemicals. This information can be useful for separating ethanoic acid from mixtures containing these chemicals, as the different boiling points can be exploited through distillation or other separation techniques.
Additionally, the boiling point of ethanoic acid can be used to determine its purity. If the measured boiling point of a sample of ethanoic acid is significantly different from the standard boiling point, it may indicate the presence of impurities or other contaminants. This technique can be useful in quality control or research settings where precise measurements of chemical properties are required.
Finally, it is worth noting that the boiling point of ethanoic acid can be affected by the presence of catalysts, which can lower the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur and therefore lower the boiling point. This information can be useful in industrial or laboratory settings where ethanoic acid is used as a reactant or solvent, as the addition of a catalyst can help to optimize reaction conditions and increase efficiency.
Conclusion
The boiling point of ethanoic acid is a crucial property that has been extensively studied and documented. Understanding the factors that affect the boiling point, such as the presence of solutes, temperature, intermolecular forces, and the polarity of the solvent, is essential for effectively utilizing and manipulating this compound in various applications.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can measure the boiling point of ethanoic acid at home and gain a better understanding of this important chemical property. Additionally, the unique perspectives discussed in this article can provide valuable insights into the relationship between the boiling point of ethanoic acid and other chemicals, as well as its use in determining purity and optimizing reaction conditions.
References:
- Acetic acid. (n.d.). In PubChem. Retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Acetic-acid
- Why does ethyl methanoate boil after methyl ethanoate? (2022, April 8). In Chemistry Stack Exchange. Retrieved from https://chemistry.stackexchange.com/questions/164303/why-does-ethyl-methanoate-boil-after-methyl-ethanoate
- An Insight into the Boiling Point of Ethanoic Acid. (2021, December 7). In ECHEMI. Retrieved from https://www.echemi.com/cms/427857.html
- A-Level Chemistry, Specimen Paper. (n.d.). In Quizlet. Retrieved from https://quizlet.com/gb/497081628/a-level-chemistry-specimen-paper-flash-cards/
- Boiling Point. (n.d.). In Chemistry LibreTexts. Retrieved from https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Equilibria/Gas_Equilibria/Boiling_Point

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.