Bismuth is the fifth member of the pnictogen family having a molar mass of 209.9804 u. Let us focus on some uses of bismuth in different industries.
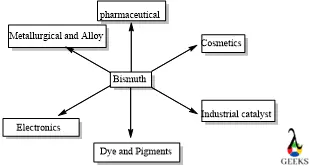
Bismuth is used in the following industry –
- Pigments
- Cosmetics
- Industrial catalyst
- Metallurgical industry
- Alloys and solder
- Electronics
- Research and Development
- Spectroscopy
Bismuth has n-type conductivity but at high temperatures, they show p-type conductivity. Now discuss the industrial uses of bismuth in the next part of the article.
Pigments
- To produce pearlescent luster in plastics, cosmetic bismuth oxychloride was used.
- Bismuth molybdate is used as paint pigments for the car and school buses.
- Bismuth oxynitrate is used as a white color pigment, also known as bismuth white or Spanish white.
- Bismuth vanadate is non-reactive paint that can be used for drawing purposes.
- Bismuth oxychloride is used in the replacement of lead carbonate pigments for the production of plastic buttons.
- Bismuth subnitrate is a component of glazes that produces iridescence and is used as a pigment in paint.
Cosmetics
- In ancient Egypt Bismuth oxychloride is used as cosmetics.
- Bismuth oxychloride (BiOCl) is sometimes used in cosmetics, as a pigment in the paint for eye shadows, hair sprays, and nail polishes
- This compound is found as the mineral bismoclite and in crystal form contains layers of atoms (see figure above) that refract light chromatically, resulting in an iridescent appearance similar to the nacre of the pearl.
Industrial catalyst
- Bismuth molybdate is used as the catalyst for the production of acrylonitrile which is first developed by Ohio in 1960.
- Iron, phosphorus, and bismuth are used as the special catalyst for the production of acrylonitrile butadiene rubber which is a monomeric unit.
- Bismuth is applied for the production of butadiene styrene plastics as catalysts.
- Bismuth acts as an electrocatalyst in the conversion of CO2 to CO.
- As a catalyst for the fluorination of aryl boronic pinacol esters through a Bi(III)/Bi(V) catalytic cycle, mimicking transition metals in electrophilic fluorination.
Metallurgical industry
- Bismuth is used as an additive for the improvement of the machinability of steel.
- Bismuth is used as a better alternative for tellurium and leads for free-machining steel due to its lower melting point and acts as a lubricant.
- Bismuth is applied for the solidification of the steel causing embrittlement.
- To increase the melting point of stainless steel 3-5% bismuth is added to it.
- Bismuth is used in applications that are required in sanitary conditions like rotors of food and beverage pumps.
- Bismuth is added to malleable cast iron to prevent its brittleness and increase its ductility.
Alloys and solder
- Bismuth-lead alloy is used as an additive to increase the machinability of aluminium.
- Bismuth is added into the aluminium-magnesium alloy to prevent cracking of the metal during the rolling process and also improve the corrosion resistance.
- Many bismuth alloys have low melting points and are found in specialty applications such as solders.
- Many automatic sprinklers, electric fuses, and safety devices in fire detection and suppression systems contain the eutectic Indium-Cadmium-lead-tin-Bismuth an alloy that melts at 47 °C.
- Low-melting alloys, such as Bi-Cd-Pb-Sn alloy which melts at 70 °C, are also used in automotive and aviation industries like jet engine turbine plates or military aircraft.
- Bismuth is used as an alloying agent in the production of malleable iron and as a thermocouple material.
- Bismuth is used as a fusible alloy that protects the fuel tank of vehicles from explosion.
- For the fire sprinkler system bismuth-base alloy is used for the trigging device.
- Tin-bismuth eutectic alloys or sodium alloys are used for making low-temperature solders which are used in electronic devices.
- In radiation bismuth-base alloys are used as protecting shields.
Electronics
- Bismuth telluride is a semiconductor and an excellent thermoelectric material. Bi2Te3 diodes are used in mobile refrigerators, CPU coolers, and as detectors in infrared spectrophotometers.
- Tin-bismuth alloys are used in the formation of metalized plastic that is used in satellite dishes for receiving signals.
Research and Development
- Bismuth compounds are tested as flame retardants for plastics.
- Some silver oxide button cells, zinc-nickel rechargeable batteries, and silver-lithium cells use bismuth as a cathode material.
- Organometal compounds of bismuth like triphenyl bismuth is used as an important reagent for making plastics.
Spectroscopy
- Bismuth germanate is a scintillator, widely used in X-ray and gamma-ray detectors.
- Bismuth tellurite is the main constituent of thermoelectric coolers which is used to stabilize the temperature of lasers and infrared detectors.
Bismuth oxide uses
Bismuth form oxide has valency +3, so the bismuth (III) oxide or Bi2O3 has five crystallographic polymorphs. let us focus on some uses of Bi2O3.
Bismuth oxide is used in the following industry –
- Electrochemical
- Ceramic
- Radiative cooling
Electrochemical
- Bismuth oxide, in its delta form, is a solid electrolyte for oxygen. This form normally breaks down below a high-temperature threshold but can be electrodeposited well below this temperature in a highly alkaline solution.
- Dibismuth trioxide is commonly used to produce the “Dragon’s eggs” effect in fireworks, as a replacement for red lead.
- Bismuth oxide is added to zinc oxide to produce varistors which are used as lighting and surge protectors in high-voltage applications.
Ceramic
- Bismuth oxide is applied to ceramic permanent magnets (ferrites) to increase their magnetic field and strengthen the ceramic.
- Bismuth oxide can increase the specific gravity and refractive index of the glass.
Radiative cooling
- Bismuth oxide was used to develop a scalable colored surface high in solar reflectance and heat emissivity for passive radiative cooling.
- The main applications of bismuth oxide nanoparticles are electrochemical applications, such as in the electrolyte or cathode of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC).
Conclusion
Bismuth is the group 15th element that has a metallic character and very good alternative to lead metal. Bismuth oxide has five different crystallographic forms which are used in different industries for their different melting temperature and lattice structure.

Hi……I am Biswarup Chandra Dey, I have completed my Master’s in Chemistry from the Central University of Punjab. My area of specialization is Inorganic Chemistry. Chemistry is not all about reading line by line and memorizing, it is a concept to understand in an easy way and here I am sharing with you the concept about chemistry which I learn because knowledge is worth to share it.