In this article, we will learn about Possessive Plural Nouns and their uses with 30+ examples. With the help of these examples, we will learn how to use these nouns in grammar and our daily lives.
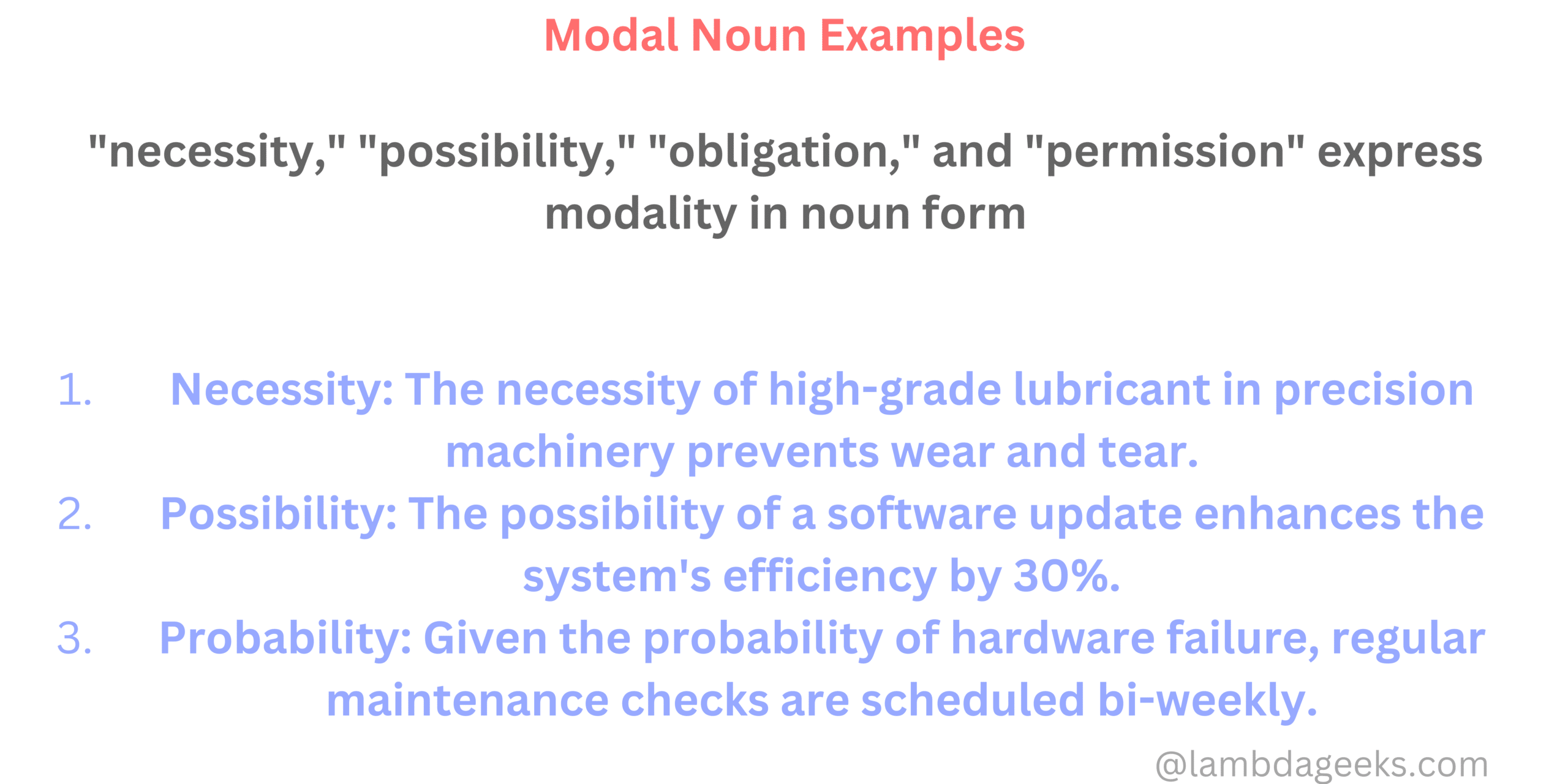
Possessive plural nouns examples are those that are in the plural form, and those plural nouns possess something. The plural nouns possess some commodity, thing, or person.
Given below is a list that will practically help you understand the concept through possessive plural nouns examples.
1. It was the dogs’ pedigree kept in the kitchen.
In this sentence, the word dogs’ comes under possessive plural nouns examples. The ‘s’ in dogs represent plural form and the apostrophe shows possession by the dog.
2. It was the primary teachers’ staffroom upstairs.
In this sentence, the word teachers’ comes under possessive plural nouns examples. The ‘s’ in the word teachers shows plural form. The apostrophe in teachers’ further shows belongingness by the teachers. The staffroom belongs to the teachers.
3. In the closet, my sisters’ old toys made me nostalgic.
The word sisters’ in this sentence depicts a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in sisters’ depicts plural form whereas the apostrophe in sisters’ depicts possession. The old toys belonged to her sisters.
4. My friends’ gifts came one day before my birthday.
The word friends’ in this sentence depicts a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in friends’ depicts a plural form whereas the apostrophe after ‘s’ shows possession. Gifts were given by her friends for her birthday.
5. The farm guards’ children were taking a stroll in the afternoon cool breeze.
The word guards’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in guards represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. It was the guards’ children that were strolling in the afternoon.
6. The bikers’ helmets got lost in the crowd.
The word bikers’ in this sentence comes under possessive plural nouns examples. The ‘s’ in bikers represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The helmets belonged to the bikers that got lost in the crowd.
7. She dropped the boys’ books.
The word boys’ in this sentence comes under possessive plural nouns examples. The ‘s’ in boys represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The books belonged to the boys that were dropped.
8. I wore my sister’s black faux leather jacket.
The word sisters’ in this sentence comes under possessive plural nouns examples. The ‘s’ in sisters represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The black faux jacket belonged to her sister which is also a noun.
9. I stood by my favorite trees’ shade near the bus stand.
The word trees’ in this sentence comes under possessive plural. The ‘s’ in trees represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The shade was given by the trees under which she took shelter.
10. She switched her friends’ gifts with one box of chocolates.
The word friends’ in this sentence comes under possessive plural nouns examples. The ‘s’ in friends represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The gifts were given by her friends that she switched with a box of chocolates.
11. The packed bottles’ owners helped the thirsty and poor.
The word bottles’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in bottles represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The owners of the bottles helped to quench the thirst of the poor and thirsty.
12. The boxes’ covers reached their respective owners before time.
The word boxes’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in boxes represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The covers belonged to the boxes that reached their respective owners.
13. The mattresses’ covers were not available on the market.
The word mattresses’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘es’ in mattresses represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The covers belonged to the mattresses that were unavailable in the market.
14. The ships’ shaft broke in the middle of the sea.
The word ships’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in ships represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The shaft belonged to the ship that broke in the middle of the sea.
15. The drafters’ drafts were not up to the mark.
The word drafters’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in drafters represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The drafts were written by the drafters which did not meet the expectations of a correct draft.
16. The school uniforms’ length was too short.
The word uniforms’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in uniforms represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The uniforms belonged to a particular school that were too short.
17. A boutiques’ logo can picture flowers to make it more attractive.
The word boutiques’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in boutiques represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The logo of the boutique can picture flowers to make it attractive and catching.
18. A peoples’ government is of the people, for the people, and by the people.
The word peoples’ in this sentence is an example of a Possessive Plural Noun. The ‘s’ in peoples represent a plural form whereas the apostrophe depicts possession. The government belongs to the people.
19. The chairpersons’ seats are highly respected and honored by the other members.
The word chairpersons’ represent a plural form along with the possession of seats by the chairpersons.
20. The maimed frogs’ legs were treated individually by the doctors.
The word frogs’ represent a plural form along with the possession of legs by the frogs.
21. The scientists’ discoveries were discussed among the team members to publish the news articles.
The word scientists’ represent a plural form along with the discoveries made by the scientists.
22. The hard disks’ plates were taken for repair as there was some problem in their functioning.
The word disks’ represent a plural form along with the possession of plates by the disks.
23. The students’ marks were increasing with the efficient use of audio-visual aids.
The word students’ represent a plural form along with the marks obtained by the students.
24. The schools’ curriculums hampered the creative ideas of the students.
The word schools’ represent a plural form along with the belongingness of curriculum by the schools.
25. The fish markets’ stingy smell can make vegetarians puke.
The word markets’ represent a plural form along with the stingy smell that comes out of the fishes.
26. A lions’ dens look majestic and ferocious from far.
The word lions’ represent a plural form along with the dens belonging to the lions.
27. The chickens’ eggs consist of high-quality nutrients including minerals, vitamins, and fatty acids.
The word chickens’ represent a plural form along with the possession of their eggs.
28. The chickens’ poultry farms was far from the city.
The word chickens’ represent a plural form along with the possession of the farms by the chickens.
29. A dogs’ hair falls if they consume too many sweets.
The word dogs’ represent a plural form along with the possession of hair that falls belonging to the dogs.
30. When I was 6, I ate my dogs’ food by mistake.
The word dogs’ represent a plural form along with the possession of food by the dogs.
Read more: 30+ Predicate Noun Examples: Sentences, Uses And Detailed Explanations