Chloramines are organic and ammonia derivatives in which one or more N-H bonds have been exchanged by N-Cl bonds. Let us study in detail about Chloramine uses.
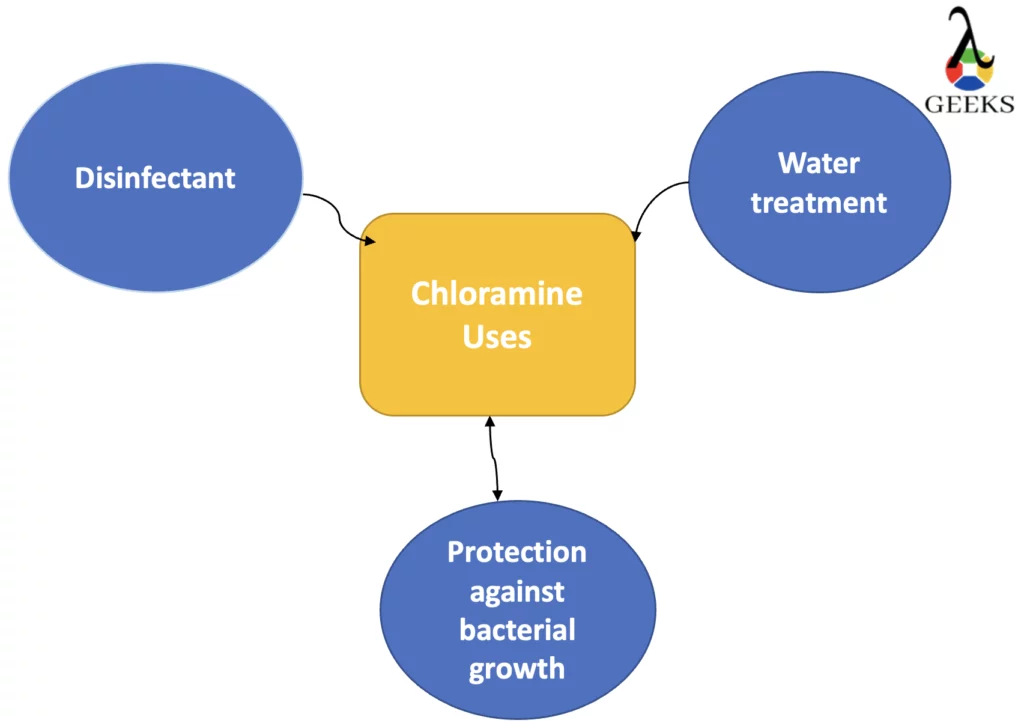
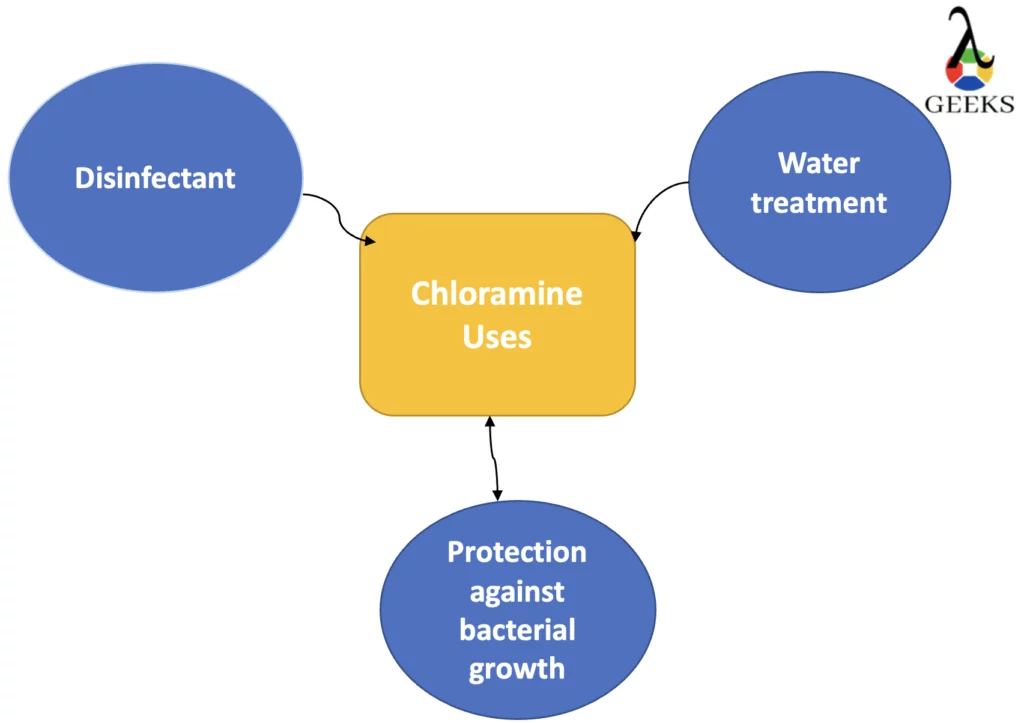
The uses of Chloramine are as follows:
- Disinfectant
- Water treatment
- Protection against bacterial growth
In this article, we will discuss about uses of Chloramines in various industries in detail.
Disinfectant
- Chloramines are used as oxidizers, disinfectants ,and bleach substitutes.
- Slower and less aggressive than hypochlorite disinfection, organic disinfectants gradually release chlorine (OCl–).
- When chlorine is used to disinfect water, chloramines can be utilised to enhance the taste and smell of the water.
- Chloramines are also utilised in cooling water systems to prevent biofouling and to disinfect drinking water and wastewater.
- Chloramine is one of the very few disinfectants that may destroy dangerous bacteria while still maintaining water quality because it is a chlorine-based compound.
Water treatment
- Drinking water is treated using chloramine. It is produced by combining ammonia and chlorine.
- Chloramine is stronger disinfectant than chlorine and is comparatively advantageous in a water utility’s distribution system.
- As water is transported through pipes to customers, chloramine offer longer-lasting disinfection.
Protection against bacterial growth
- Since chloramine residual is more stable than free chlorine in distribution systems, it provides stronger defence against bacterial regrowth.
- Similar to chlorine, chloramine is helpful at preventing biofilm, an accumulation of germs in pipes.
- Controlling biofilm has the potential to lower coliform bacteria levels as well as the corrosion of pipes driven on by biofilm.
- Many systems will encounter fewer complaints about taste and odour when utilising chloramine because chloramine does not frequently react with organic molecules.
- Chloramine is introduced to water in precise amounts to ensure that microbes are eliminated while maintaining water safety.
Conclusion
In summary, we can remark that chloramines are a type of disinfectant that is used to detoxify drinking water. They are sometimes referred to as secondary disinfection. Monochloramine is the chloramine that is most frequently used in municipal water treatment.