15 Facts on H2SO4 +Mg2Si: What, How to Balance & FAQs
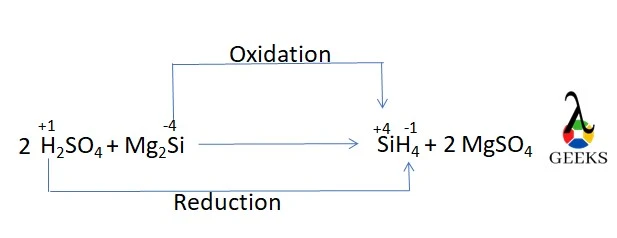
Magnesium silicide (Mg2Si) is a crystalline solid inorganic compound. Let’s see its reaction with Sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Mg2Si is water-insoluble and denser than water. It forms a face-centered cubic antifluorite structure. Si4- ion can be thought of as the main component of magnesium silicide. It reacts with acid. H2SO4 is highly soluble in water. It … Read more