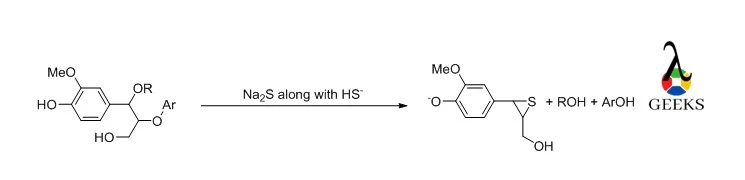
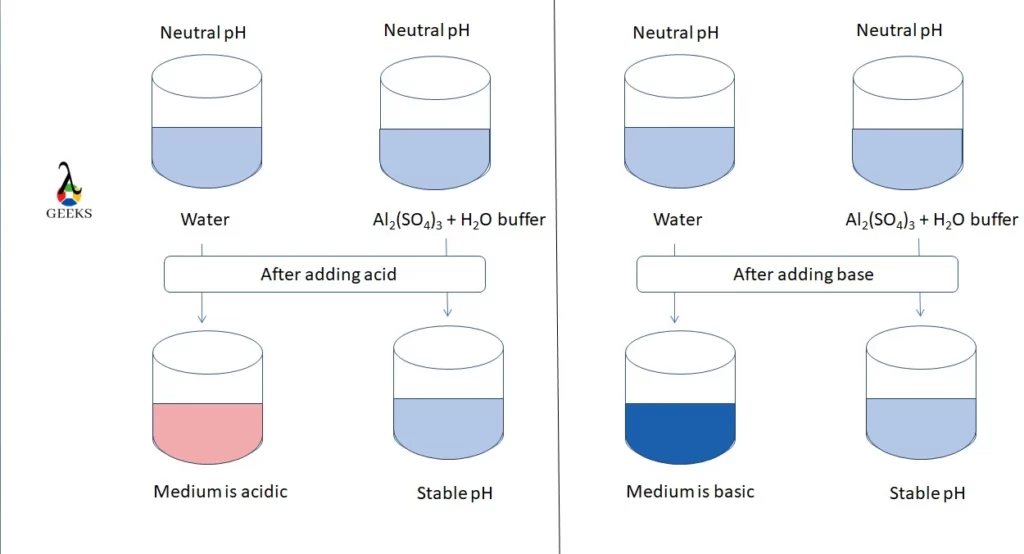
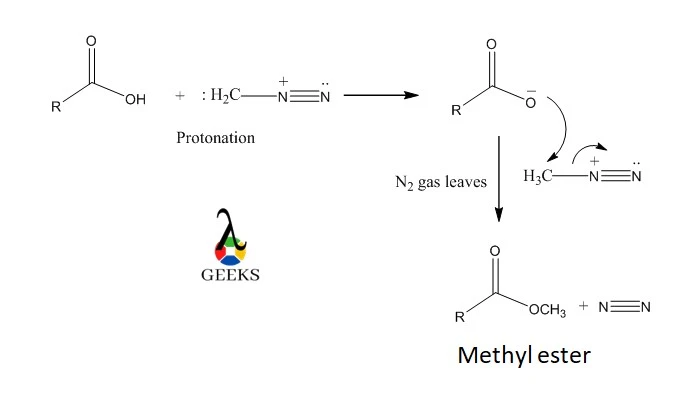
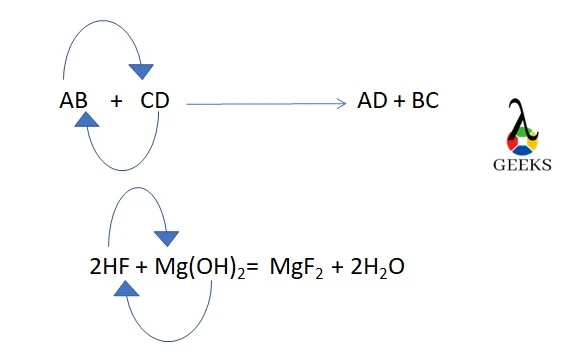
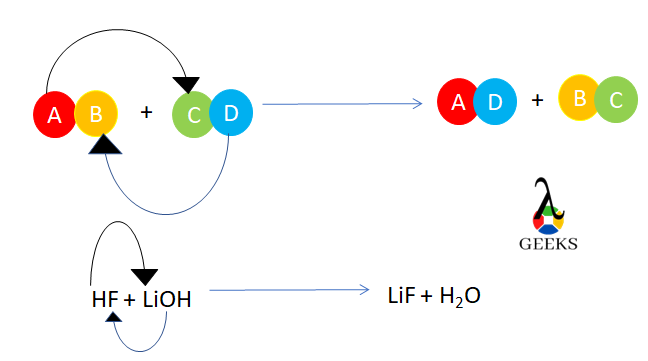
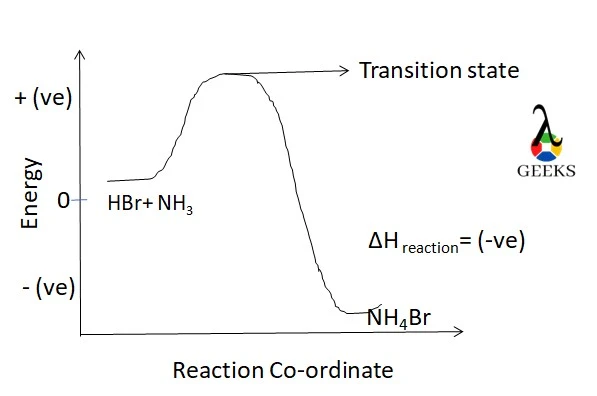
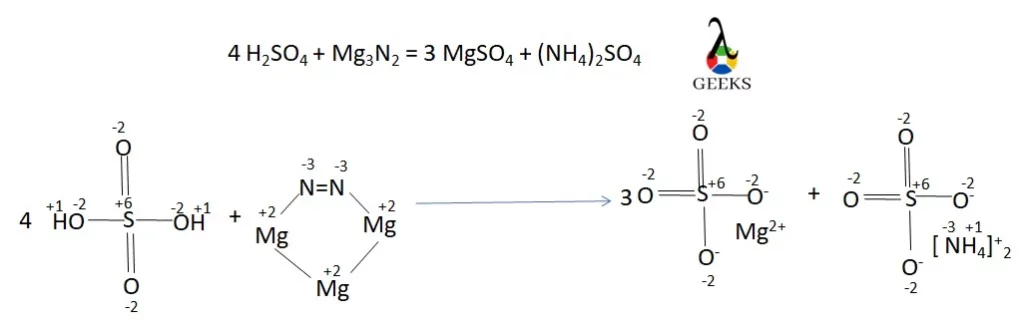
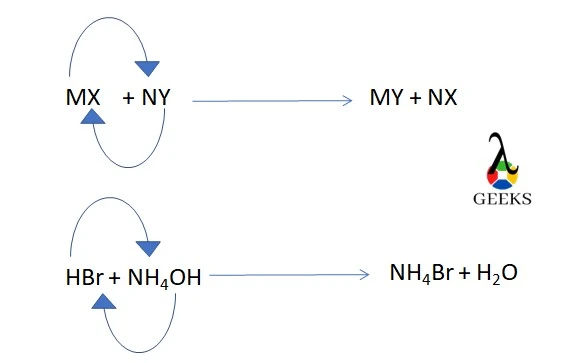
11 Sodium Sulfide Uses: Facts You Should Know!
Sodium sulfide is a hygroscopic ionic solid with the formula of Na2S. It is corrosive and has a rotten egg-like smell. Let us discuss various uses of Sodium sulfide (Na2S). Sodium sulfide is used in a variety of fields, including Na2S is readily available in the hydrated form, Na2S. 9H2O. Both anhydrous and hydrous forms … Read more