In this article, “are ketones acidic”, the acidity of ketones and the comparison of acidity with other compounds are discussed briefly.
Ketones are those compounds, in which two alkyl or aryl groups are attached with the carbonyl carbon. The hydrogen atoms attached with the alkyl or aryl group is acidic. Due to the presence of this acidic hydrogen, ketones are acidic in nature. But the acidity of ketone is not as much as in any acids (pka of ketone is 17 to 21).
Let’s focus on the following topics on the acidity of ketone.
Why are ketones acidic?
Ketones are acidic compound (pka =20). To explain the acidity of ketone, the definition of acid-base (Bronsted-Lowry Scheme) will be remembered that an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. After dissociation of an acid, conjugate base and H+ ion will be generated.
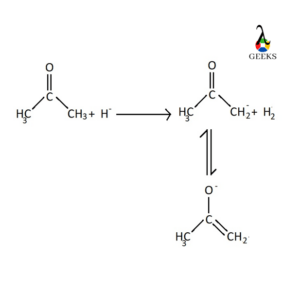
From the above diagram it can be seen that, ketone donates its one hydrogen and form CH3 –CO- CH2– (enolate ion). This is the conjugate base of ketone (acetone). In the above example, hydride ion (H–) acts as a base. It accepts the hydrogen which acetone donates in the above reaction. The resulting enolate ion gets the stabilization due to delocalization of negative charge from less electronegative carbon atom to more electronegative oxygen atom. Double bond will be replaced from C-O bond to C-C single bond after the delocalization.
But the enolate ion is not as stable as ketone. The enol and ketone are in a chemical equilibrium which helps the enol to release one hydrogen for converting the enol to an enolate.
Are ketones acidic in water?
The pka value of water and ketone is 16 and 20 respectively. Pka value indicates water as more acidic than ketone (substance having lower pka is more acidic).
Ketone reacts with water in presence of an acid. Ketone is also soluble in water due to formation of hydrogen bond with water. After reacting with water in presence of acid, ketone forms geminal-diol and an equilibrium is established between the ketone and the product (geminal-diol).
The steps of the above reaction are described below-
- Protonation of the carbonyl group: carbonyl group (C=O) is protonated by the hydrogen atom of H3O+ (formed by the reaction between water and acid).
- Nucleophilic attack by water: In the second step, the lone pair of oxygen attacks in the protonated carbonyl centre.
- Deprotonation: One of the hydrogen atom from the water molecule (added to the carbonyl centre) is eliminated and the desired product geminal-diol is formed.

Are ketones more acidic than carboxylic acids?
No, ketones are not more acidic than carboxylic acid. The pka value of ketone and carboxylic acid is 20 and 3-5 respectively.
The reason of more acidity of carboxylic acid is the stabilization of its conjugate base. The conjugate base of carboxylic acid (carboxylate ion) is stabilized due to two equivalent resonance. But the conjugate bas of ketone (enolate ion) gains the stabilization by only one resonance. Besides that, in carboxylic acid, O-H group is directly attached with the carbonyl carbon centre. Due to electrophilicity of this centre, the O-H bond of carboxylic acid becomes polar and hydrogen ion elimination will be more facile.
In ketone, no such O-H group is present. Alkyl or aryl groups are directly attached with the carbonyl carbon center. Thus, proton transfer will not be so much favorable with respect to carboxylic acids.
There are some reagents (nucleophiles) like organometallic reagents, acetylides, nitriles, amines which occurs carbonyl addition with ketone but deprotonates a carboxylic acid. This is also an evidence that the acidity of carboxylic acids are greater than ketone.
Are ketones more acidic than esters?
Yes, ketones are more acidic than ester. Pka value confirms the more acidic nature of ketone with respect to ester. The pka value of ketone and ester is nearly equals to 20 and 25 respectively.
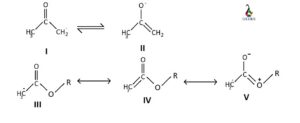
In the above image the resonance structure of the enolate ion of both the ketone and ester are described. In case of ester, there is an additional conjugation structure (V). In this structure the alkoxy group (OR group) donates electrons to the carbonyl carbon (C=O).
This electron donation destabilizes this resonance structure because the formation of negative charge on carbon connected to the another side of carbonyl carbon will be disfavored. The resonance structure IV contributes less with respect to V. Thus, the enolate ion of ester is getting destabilized than the enolate ion of ketone because in ketone no such disfavored resonance structure is formed.
The less stable conjugate base decreases the acidity of the ester with comparing to ketone.
Are ketones more acidic than aldehydes?
No, ketones are less acidic than an aldehyde. Pka of an aldehyde and ketone is 17 and 20 respectively. As lower pka value indicates more acidity, aldehyde is more acidic with respect to ketone.
The basic difference between aldehyde and ketone is the replacement of one alkyl group of ketone by hydrogen in aldehyde. Alkyl groups are generally weakly electron donor in nature due to having +I effect. This electron donation property destabilizes the anion because the alkyl group are pushing the electron density to wards the electron rich species (carbanion).
But in aldehyde, no such alkyl group is present who can push the electron density towards the carbanion and destabilizes the enolate ion.
Thus, the conjugate base of aldehyde is more stable due to absence of the above destabilizing effect with comparing to the conjugate base of ketone.
Why are ketones more acidic than alkanes?
The C-H bond of a ketone is more acidic than the C-H bond of an alkane because the pka value of ketone and alkene is approximately 20 and 50 respectively.
This difference in pka demonstrated that the stabilization of conjugate base due to electron delocalization in ketone. The enolate ion of ketone is resonance stabilized. But this resonance is absent in alkane. Due to having C=O group the hydrogen ion from one alkyl group can be eliminated easily. Because C=O group is electrophilic in nature. It attracts the electron density towards itself and hydrogen ion elimination will be facile.
But in alkane no such carbonyl group is present and the resonance of enolate can not be taken place. Thus, the conjugate base of alkane has no stabilization factor. Thus, it shows less acidity than ketone.

Hello,
I am Aditi Ray, a chemistry SME on this platform. I have completed graduation in Chemistry from the University of Calcutta and post graduation from Techno India University with a specialization in Inorganic Chemistry. I am very happy to be a part of the Lambdageeks family and I would like to explain the subject in a simplistic way.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditi-ray-a7a946202