Antimony with the atomic number 51 and the chemical symbol Sb is a metalloid. Let us study its electronegativity and ionization energy in detail.
Antimony belongs to group 15, 5th period, and p-block of the periodic table. The metalloid is a lustrous silvery-white solid at room temperature. It is commonly found in nature as sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3).
All the important features of electronegativity and ionization energy of antimony will be clear as we proceed.
Electronegativity of antimony trichloride
The electronegativity of antimony chloride is not possible as electronegativity values are available in the database only for an element, not a compound. It is an inorganic chloride salt that is used in the synthesis of pure antimony trioxide.
Antimony ionization energy
The atomic number of antimony is 51, and the electron configuration is [Kr]4d105s25p3.
- The first ionization energy of antimony is 830.58 kJ/mole which is to be provided when the first electron is removed from the 5p orbital.
- The second ionization energy of antimony is 1604.20 kJ/mole which is to be provided when the second electron is removed from the 5p orbital.
- The third ionization energy of antimony is 2443.35 kJ/mole which is to be provided when the third electron is removed from the 5p orbital.
- The fourth ionization energy of antimony is 4226.40 kJ/mole which is to be provided when the fourth electron is removed from the 5s orbital.
- The fifth ionization energy of antimony is 5307.00 kJ/mole which is to be provided when the fifth electron is removed from the 5s orbital.
Antimony ionization energy graph
The ionization energy graph of antimony is drawn by taking ionization energy (in kJ/mole unit) in the y-axis and the ionization number in the x-axis.
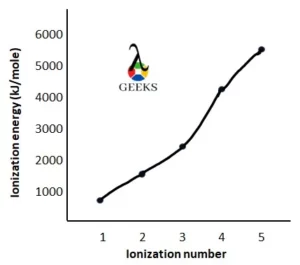
Antimony first ionization energy
The first ionization energy of antimony is 830.58 kJ/mole which is to be supplied to remove the first valence electron from 5p orbital.
Third ionization energy for antimony
The third ionization energy of antimony is 2443.35 kJ/mole which is to be supplied to remove the third valence electron from the 5p orbital.
Antimony and bismuth ionization energy
Antimony and bismuth belong to the fifth period and sixth period respectively but both of them belong to group 15. The ionization energy of antimony is higher than that of bismuth. The explanation behind this observation is given below.
| First ionization energy of antimony | First ionization energy of bismuth | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 830.58 kJ/mole | 702.95 kJ/mole | The electronic configuration of antimony is [Kr]4d105s25p3, and that of bismuth is [Xe]4f145d104d106s26p3. Removal of an outermost electron from 5p orbital requires more energy than removal of the same from 6p orbital, as in the second case electron is far from the nucleus. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, antimony is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. It is mostly used today for fireproofing materials to increase the hardness of alloys, semiconductors, and microelectronics. It is hardly found in elemental form.

Hello, I am Tuluma Das, Completed my Ph.D. in Organic Chemistry from the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science. I have a total of 9 years of research experience including a Ph.D. and Postdoc and 3 years of teaching experience. I have published 7 papers so far in international journals. Let’s connect through Linkedin :