Acetone, a versatile and widely used organic compound, is a colorless, volatile, and flammable liquid with the chemical formula (CH3)2CO or C3H6O. As the simplest and smallest ketone, acetone is a common solvent employed in various industries, including as the primary ingredient in nail polish remover and in the manufacturing of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals.
Understanding Acetone Density
The density of a substance, such as acetone, is a measure of its mass per unit volume. The density of acetone is typically reported as 0.7845 g/cm³ or 0.7845 g/mL at 20°C (68°F). This means that one cubic centimeter or one milliliter of acetone has a mass of 0.7845 grams. It is crucial to note that the density of a substance can vary with temperature, so it is essential to specify the temperature at which the density is being measured.
Factors Affecting Acetone Density
The density of acetone can be influenced by several factors, including:
-
Temperature: As the temperature of acetone increases, its density decreases. This is due to the thermal expansion of the liquid, which causes the molecules to move further apart, reducing the mass per unit volume.
-
Pressure: Increasing the pressure on acetone can slightly increase its density, as the molecules are compressed closer together.
-
Impurities: The presence of other substances, such as dissolved gases or suspended particles, can affect the density of acetone. These impurities can either increase or decrease the overall density, depending on their own densities.
Calculating Acetone Density
To determine the density of acetone in a laboratory setting, a common method is to measure the volume of the liquid in a graduated cylinder and its mass on a balance. The density can then be calculated by dividing the mass by the volume, as shown in the following equation:
Density = Mass / Volume
For example, if you measure 100 mL of acetone and find that it has a mass of 78.45 g, you can calculate the density as follows:
Density = 78.45 g / 100 mL = 0.7845 g/mL
Other methods for determining the density of liquids, such as using a hydrometer or a picometer, or using a volumetric flask to measure the volume, can also be employed.
Acetone Density at Different Temperatures
The density of acetone is known to vary with temperature. The following table provides the density of acetone at different temperatures:
| Temperature (°C) | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.7929 |
| 10 | 0.7887 |
| 20 | 0.7845 |
| 30 | 0.7803 |
| 40 | 0.7761 |
| 50 | 0.7719 |
To calculate the density of acetone at a specific temperature, you can use the following formula:
Density = 0.7845 – 0.0002 × (T – 20)
Where:
– T is the temperature in degrees Celsius (°C)
– Density is in g/cm³
For example, to calculate the density of acetone at 25°C, you would use the formula:
Density = 0.7845 – 0.0002 × (25 – 20)
Density = 0.7845 – 0.0002 × 5
Density = 0.7845 – 0.001
Density = 0.7835 g/cm³
Measuring Acetone Density
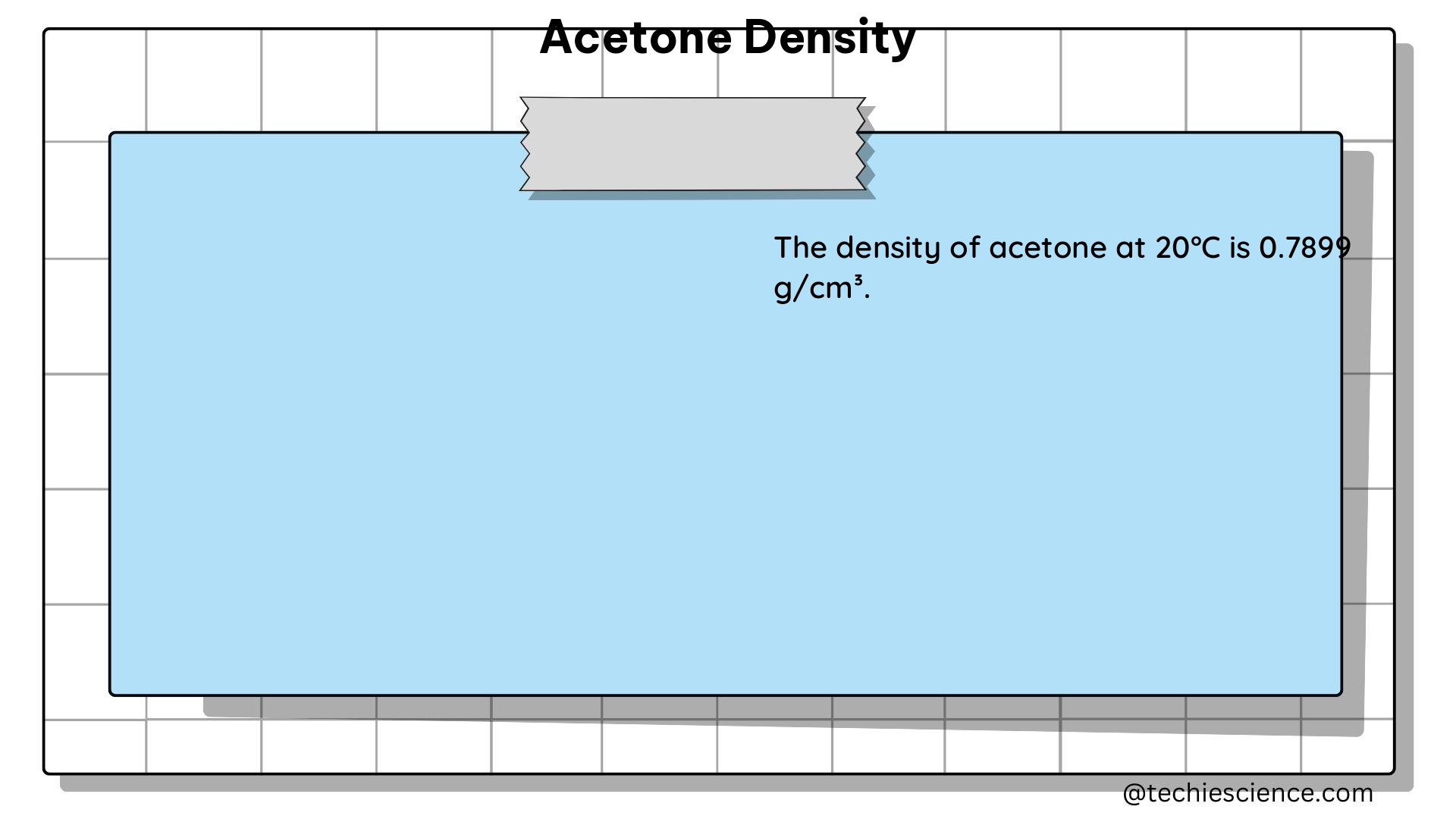
There are several methods for measuring the density of acetone, each with its own advantages and limitations. The choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the application, the available equipment, and the desired level of accuracy.
Graduated Cylinder and Balance Method
As mentioned earlier, the most common method for measuring the density of acetone in a laboratory setting is the graduated cylinder and balance method. This involves the following steps:
- Measure the volume of acetone in a graduated cylinder.
- Weigh the mass of the acetone using a balance.
- Calculate the density by dividing the mass by the volume.
This method is relatively simple and straightforward, but it requires careful measurements to ensure accuracy.
Hydrometer Method
Another method for determining the density of acetone is the hydrometer method. A hydrometer is a device that measures the relative density of a liquid by measuring the depth to which it sinks in the liquid. To use a hydrometer to measure the density of acetone, you would:
- Fill a container with the acetone sample.
- Carefully lower the hydrometer into the container, ensuring it is fully submerged.
- Read the density value directly from the hydrometer scale.
Hydrometers are often used in industrial settings, as they provide a quick and convenient way to measure the density of liquids.
Picnometer Method
The picnometer method is a more precise way to measure the density of acetone. A picnometer is a small, calibrated glass bottle with a ground-glass stopper. To use a picnometer to measure the density of acetone:
- Weigh the empty, clean, and dry picnometer.
- Fill the picnometer with the acetone sample, ensuring there are no air bubbles.
- Weigh the picnometer filled with the acetone sample.
- Calculate the density by dividing the mass of the acetone sample by the volume of the picnometer.
The picnometer method is generally more accurate than the graduated cylinder and balance method, as it eliminates the need to measure the volume of the liquid separately.
Density Meter Method
For more precise measurements of acetone density, a density meter can be used. Density meters, also known as digital density meters or oscillating U-tube density meters, use the principle of oscillating U-shaped glass or metal tubes to determine the density of liquids.
To measure the density of acetone using a density meter:
- Calibrate the density meter according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Introduce the acetone sample into the measurement cell of the density meter.
- The density meter will automatically measure and display the density of the acetone sample.
Density meters are highly accurate and can provide precise measurements of acetone density, often with a resolution of up to 0.00001 g/cm³.
Acetone Density Applications and Considerations
The density of acetone is an important property that is relevant in various applications and industries. Understanding and accurately measuring the density of acetone is crucial for the following reasons:
-
Quality Control: In manufacturing processes that involve acetone, such as the production of plastics or pharmaceuticals, the density of the acetone is a critical quality control parameter. Monitoring the density can help ensure the consistency and purity of the final product.
-
Solvent Mixtures: When using acetone as a solvent, its density is essential for calculating the composition and properties of solvent mixtures, which is important in various chemical processes and formulations.
-
Environmental Monitoring: The density of acetone can be used to monitor the presence and concentration of acetone in environmental samples, such as air, water, or soil, which is important for environmental protection and regulatory compliance.
-
Safety Considerations: The density of acetone is a relevant factor in the safe handling and storage of the chemical, as it can affect the flammability and volatility of the substance.
-
Forensic Applications: The density of acetone can be used in forensic investigations, such as the analysis of trace evidence or the detection of acetone in biological samples.
It is important to note that the density of acetone can be affected by various factors, such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities. Therefore, it is crucial to specify the conditions under which the density is measured and to consider these factors when using or interpreting the density data.
Conclusion
Acetone, a versatile and widely used organic compound, has a well-defined density that is typically reported as 0.7845 g/cm³ or 0.7845 g/mL at 20°C (68°F). However, the density of acetone can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities.
Understanding and accurately measuring the density of acetone is crucial in various applications, including quality control, solvent mixture calculations, environmental monitoring, safety considerations, and forensic investigations. By using the appropriate measurement methods, such as the graduated cylinder and balance method, the hydrometer method, the picnometer method, or the density meter method, researchers and professionals can obtain reliable and precise data on the density of acetone.
This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed exploration of the factors affecting acetone density, the methods for measuring it, and the importance of this property in various applications. By mastering the concepts and techniques presented here, you can become a true expert in the field of acetone density and contribute to the advancement of research, development, and practical applications in your respective fields.
References:
- How to Find the Density of Acetone ( (CH3)2CO or C3H6O) – YouTube. (2022-06-30). Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iufumVTgE20
- Acetone | CH3-CO-CH3 or C3H6O | CID 180 – PubChem. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Acetone
- How to calculate the density of acetone at different temperatures … – Homework.study.com. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://homework.study.com/explanation/how-to-calculate-the-density-of-acetone-at-different-temperatures-show-your-explanation.html
- Toxicological Profile for Acetone. (June 2022). Retrieved from https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp21.pdf
- Density of Acetone at Different Temperatures – Engineering ToolBox. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/acetone-density-temperature-d_1636.html
- Density of Liquids – Chemistry LibreTexts. (2020-08-27). Retrieved from https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Analytical_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_(Analytical_Chemistry)/Quantitative_Analysis/Density_and_Concentration/Density_of_Liquids

The lambdageeks.com Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the lambdageeks.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.