Introduction:
When two quantities are inversely proportional, it means that as one quantity increases, the other quantity decreases, and vice versa. In other words, the relationship between the two quantities is such that when one goes up, the other goes down, and when one goes down, the other goes up. This type of relationship is commonly seen in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and economics. Understanding the concept of inversely proportional is crucial for analyzing and solving problems involving these types of relationships.
Key Takeaways:
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
|---|---|
| Value 1 | Value 2 |
| Value 3 | Value 4 |
| Value 5 | Value 6 |
Understanding Inversely Proportional
In the realm of mathematics and physics principles, there exists a fascinating concept known as inversely proportional. This concept describes a mathematical relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable corresponds to a decrease in another, and vice versa. In other words, as one variable increases in value, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is often represented by a proportionality constant, denoted as ‘k’, which helps quantify the inverse variation between the variables.
Definition of Inversely Proportional
Inversely proportional, also referred to as inverse variation, is a quantitative analysis of the relationship between two variables. It signifies that when one variable increases in value, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed using the formula:
y = k/x
Here, ‘y’ and ‘x’ represent the dependent variables, and ‘k’ is the constant of variation. The constant ‘k‘ remains the same throughout the relationship and determines the nature of the inverse proportionality. It is important to note that the value of ‘k’ should not be zero, as it would result in an undefined relationship.
Inversely Proportional Symbol
To represent the inverse proportionality between variables, the symbol ‘∝’ is commonly used. This symbol indicates that the variables are inversely proportional to each other. For example, if ‘x’ and ‘y’ are inversely proportional, it can be represented as:
x ∝ 1/y
This symbol serves as a concise way to express the inverse relationship between variables, making it easier to understand and interpret mathematical models.
Inversely Proportional Equation
The inverse proportionality between two variables can be mathematically expressed using an algebraic expression or equation. As mentioned earlier, the equation for an inverse relationship is:
y = k/x
In this equation, ‘y’ represents one variable, ‘x’ represents another variable, and ‘k’ represents the constant of variation. The equation signifies that the product of the variables remains constant. As ‘x’ increases, ‘y’ decreases, and vice versa, while maintaining a constant ratio determined by ‘k’. This relationship can be graphically represented by a curved line, indicating the inverse nature of the proportionality.
To further understand the concept of inverse proportionality, it is helpful to consider real-life examples. One such example is the relationship between the speed of a vehicle and the time it takes to travel a certain distance. As the speed increases, the time taken to cover the distance decreases, and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be represented using the equation mentioned above.
In conclusion, understanding inversely proportional relationships is crucial in various scientific laws and mathematical models. By recognizing the inverse variation between variables and utilizing the appropriate equations, scientists and mathematicians can analyze and interpret complex phenomena. The concept of inverse proportionality provides a valuable tool for quantitative analysis, allowing us to explore the intricate interplay between different quantities in a wide range of fields.
Inversely Proportional in Mathematics

In mathematics, the concept of inversely proportional refers to a mathematical relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable leads to a decrease in another variable, and vice versa. This relationship is often represented by a proportionality constant, denoted as ‘k’, which quantifies the inverse variation between the variables.
What Does Inversely Proportional Mean in Maths
When two variables are inversely proportional, it means that as one variable increases in value, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed using the formula:
y = k/x
Here, ‘x’ and ‘y’ represent the two variables, and ‘k’ is the constant of variation. The value of ‘k’ remains constant throughout the relationship, indicating the inverse proportionality between the variables.
Inversely Proportional Formula in Mathematics
The formula for inverse proportionality in mathematics is given by:
y = k/x
In this formula, ‘y’ and ‘x’ represent the two variables involved in the inverse relationship, and ‘k’ represents the constant of variation. The value of ‘k’ remains the same for any given pair of ‘x’ and ‘y’ values, indicating the inverse proportionality between the variables.
Examples of Inversely Proportional in Mathematics
To better understand the concept of inverse proportionality, let’s consider a few examples:
Speed and Time: The speed at which a car travels is inversely proportional to the time it takes to reach a destination. As the speed of the car increases, the time taken to reach the destination decreases, and vice versa.
Number of Workers and Time Taken: The time taken to complete a task is inversely proportional to the number of workers assigned to it. If more workers are assigned to a task, the time taken to complete it decreases, and if fewer workers are assigned, the time taken increases.
Distance and Intensity of Light: The intensity of light decreases as the distance from the light source increases. This is an example of inverse proportionality, where the intensity of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
In each of these examples, the relationship between the variables can be represented using the formula y = k/x, where ‘y’ and ‘x’ represent the dependent variables, and ‘k’ represents the constant ratio or proportionality constant.
In summary, inverse proportionality in mathematics describes a relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable leads to a decrease in another variable, and vice versa. This relationship can be represented using the formula y = k/x, where ‘k’ is the constant of variation. Understanding inverse proportionality is essential for quantitative analysis, as it allows us to model and analyze various scientific laws and phenomena using mathematical expressions.
Inversely Proportional in Physics
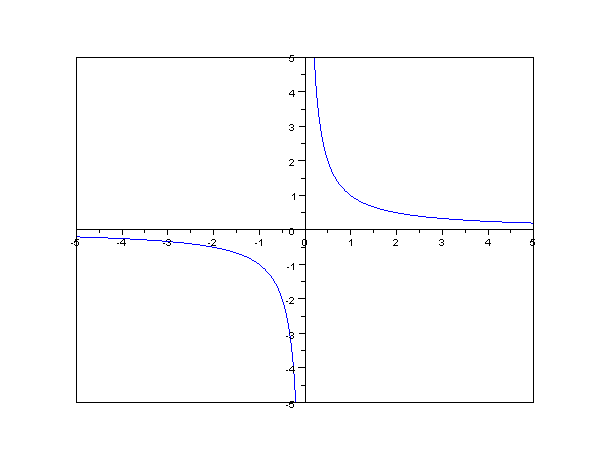
What Does Inversely Proportional Mean in Physics
In physics, when two variables have an inversely proportional relationship, it means that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. This mathematical relationship is also known as inverse variation or inverse proportionality. It is a fundamental concept in physics principles and is often used in quantitative analysis.
To understand inverse proportionality, let’s consider an example. Suppose we have two variables, x and y, and they are inversely proportional. As the value of x increases, the value of y decreases, and when x decreases, y increases. This relationship can be represented by the formula y = k/x, where k is the proportionality constant. The value of k remains constant throughout the relationship.
Examples of Inversely Proportional in Physics
To further illustrate the concept of inverse proportionality, let’s explore a few examples:
Speed and Time: The speed of an object and the time it takes to travel a certain distance are inversely proportional. As the speed of an object increases, the time it takes to cover the distance decreases. For example, if you increase your driving speed, you will reach your destination in less time.
Pressure and Volume: In the field of thermodynamics, the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional. When the volume of a gas decreases, the pressure increases, and when the volume increases, the pressure decreases. This relationship is described by Boyle’s Law.
Force and Distance: In physics, the force applied to an object and the distance over which it is applied are inversely proportional. If you apply a constant force to an object, the distance it moves will be inversely proportional to the force. For example, if you push a box with a constant force, the distance it moves will be shorter if the force is increased.
Inversely Proportional Meaning in Physics
Inversely proportional in physics means that two variables have a reciprocal relation, where an increase in one variable corresponds to a decrease in another variable, and vice versa. This relationship can be represented by an algebraic expression or a mathematical model. Inverse proportionality is often depicted graphically as a curved line, as opposed to a straight line in direct proportionality.
The ratio between the two variables in an inverse proportion remains constant and is known as the constant of variation or the proportionality constant. It is denoted by the symbol k. The value of k represents the relationship between the variables and can be used to calculate one variable when the other is known.
In summary, inverse proportionality is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable corresponds to a decrease in another variable, and vice versa. It is represented by a mathematical formula, a graph, or an algebraic expression. Understanding inverse proportionality allows us to analyze and quantify various phenomena in the natural world.
Inversely Proportional Relationships
Inversely Proportional vs Directly Proportional
When studying mathematical relationships, we often come across two types: inversely proportional and directly proportional. Inversely proportional relationships are characterized by a negative correlation between two variables, while directly proportional relationships exhibit a positive correlation. In this section, we will focus on understanding inversely proportional relationships and how they differ from their directly proportional counterparts.
Inversely Proportional and Directly Proportional Relationship
In an inversely proportional relationship, as one variable increases, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. This means that the two variables change in opposite directions. On the other hand, in a directly proportional relationship, both variables change in the same direction. Understanding these relationships is crucial in various fields, including physics, where principles of proportionality play a significant role.
To analyze inversely proportional relationships quantitatively, we use the concept of a proportionality constant, often denoted as ‘k’. This constant represents the ratio between the two variables and remains constant throughout the relationship. By using this constant, we can express the relationship between the variables through an algebraic expression or a mathematical model.
When Y is Inversely Proportional to X
Let’s consider a scenario where ‘Y’ is inversely proportional to ‘X’. As ‘X’ increases in value, ‘Y’ decreases, and when ‘X’ decreases, ‘Y’ increases. The proportionality constant ‘k’ is used to represent this relationship. It is important to note that the value of ‘k’ will vary depending on the specific relationship being analyzed.
To better understand this inverse variation, we can represent it graphically. When plotting the values of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ on a graph, we observe a curved line instead of a straight line. This curved line indicates the inverse relationship between the two variables. Additionally, we can also represent the inverse variation using the reciprocal of ‘X’ and ‘Y’. This reciprocal relation helps us visualize the inverse proportionality more clearly.
In summary, an inversely proportional relationship is characterized by a negative correlation between two variables. As one variable increases, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. The proportionality constant ‘k’ represents the relationship between the variables and can be used to express the relationship through an algebraic expression or a mathematical model. By understanding inverse proportionality, we can analyze and interpret various scientific laws and phenomena.
Inversely Proportional in Real-Life Scenarios
In the world of physics, there are many mathematical relationships that help us understand the behavior of various quantities. One such relationship is called “inversely proportional.” This term refers to a situation where two variables have a reciprocal relation, meaning that as one variable increases in value, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. Inversely proportional relationships can be found in various real-life scenarios, and they are governed by certain scientific laws and principles.
Why Force is Inversely Proportional to Square of Distance
One example of an inversely proportional relationship is the relationship between force and distance. According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the force of attraction between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This means that as the distance between two objects increases, the force of attraction between them decreases, and as the distance decreases, the force of attraction increases. This principle helps explain why objects fall towards the Earth and why planets orbit around the Sun.
How is Pressure Inversely Proportional to Volume
Another example of an inversely proportional relationship is the relationship between pressure and volume. According to Boyle’s law, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, assuming the temperature and the amount of gas remain constant. This means that as the volume of a gas increases, the pressure it exerts decreases, and as the volume decreases, the pressure increases. This principle is utilized in various applications, such as scuba diving, where changes in pressure affect the volume of air in a diver’s lungs.
Why is Current Inversely Proportional to Resistance
A third example of an inversely proportional relationship is the relationship between current and resistance in an electrical circuit. According to Ohm’s law, the current flowing through a conductor is inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. This means that as the resistance of a conductor increases, the current flowing through it decreases, and as the resistance decreases, the current increases. This principle is fundamental in understanding and designing electrical circuits, as it helps determine the flow of current and the behavior of various components.
In all these examples, the inverse proportionality is represented by a proportionality constant, often denoted as “k.” This constant relates the values of the two variables in an inverse ratio. It is important to note that the value of “k” remains constant throughout the relationship, regardless of the specific values of the variables. This constant of variation allows us to quantitatively analyze and represent the inverse proportionality using mathematical models and algebraic expressions.
To visually represent an inversely proportional relationship, we can use a graph. In a graph, an inverse proportionality is represented by a curved line rather than a straight line. The shape of the curve depends on the specific relationship between the variables. Additionally, the reciprocal of the proportionality constant “k” can also be used to represent the inverse relationship.
In conclusion, inversely proportional relationships are prevalent in various real-life scenarios and are governed by scientific laws and principles. Understanding these relationships allows us to make quantitative analyses and predictions about the behavior of different quantities. Whether it’s the force of gravity, the pressure of a gas, or the flow of current in an electrical circuit, inverse proportionality plays a crucial role in our understanding of the physical world.
Inversely Proportional in Different Fields
In various fields, such as physics and mathematics, we often come across the concept of inverse proportionality. This mathematical relationship describes how two variables change in opposite directions. When one variable increases, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. In this article, we will explore three examples of inverse proportionality in different fields: acceleration and mass, rate of diffusion, and capacitance and distance.
Why is Acceleration Inversely Proportional to Mass?
Acceleration is a fundamental concept in physics that measures the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is directly related to the force applied to an object and inversely proportional to its mass. In simpler terms, when the mass of an object increases, its acceleration decreases, and when the mass decreases, the acceleration increases. This inverse relationship can be explained using the formula:
acceleration ∝ 1/mass
Here, the proportionality constant is represented by the symbol “∝”. It signifies that the acceleration is directly proportional to the reciprocal of the mass. In other words, the value of the constant of variation, denoted as “k,” remains the same for a given system.
What is Inversely Proportional to the Rate of Diffusion?
The rate of diffusion refers to how quickly particles spread out from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. In the field of chemistry, the rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular mass of the substance. This means that as the molecular mass increases, the rate of diffusion decreases, and as the molecular mass decreases, the rate of diffusion increases. Mathematically, this relationship can be expressed as:
rate of diffusion ∝ 1/√(molecular mass)
The inverse proportionality between the rate of diffusion and the square root of the molecular mass can be observed in various scientific experiments and is an essential concept in quantitative analysis.
Why is Capacitance Inversely Proportional to Distance?
Capacitance is a property of capacitors in electrical circuits that determines their ability to store electric charge. It is inversely proportional to the distance between the plates of a capacitor. When the distance between the plates decreases, the capacitance increases, and when the distance increases, the capacitance decreases. This inverse relationship can be represented by the formula:
capacitance ∝ 1/distance
The inverse proportionality between capacitance and distance is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and is utilized in various applications, such as designing capacitors for specific purposes.
In conclusion, inverse proportionality is a mathematical concept that plays a crucial role in understanding the relationships between variables in different fields. Whether it is the inverse relationship between acceleration and mass, the rate of diffusion and molecular mass, or capacitance and distance, recognizing and analyzing these inverse relationships allows us to make accurate predictions and develop mathematical models to represent real-world phenomena.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of inverse proportionality is a fundamental mathematical relationship where two variables change in opposite directions. When one variable increases, the other variable decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is expressed using the equation y = k/x, where y and x are the two variables and k is a constant. Understanding inverse proportionality is crucial in various fields, such as physics, economics, and engineering. It allows us to analyze and predict how changes in one variable will affect the other. By recognizing and applying the principles of inverse proportionality, we can make informed decisions and solve complex problems in our everyday lives.
How does the concept of inverse proportionality relate to the Axioms of Probability: Understanding the Principles?
The concept of inverse proportionality, as explained in Lambda Geeks’ article on inverse proportionality, examines the relationship between two variables where one increases as the other decreases. On the other hand, the article on Axioms of Probability: Understanding the Principles focuses on the fundamental principles that govern the mathematical field of probability. One might wonder how these two topics intersect.
Probability theory often deals with variables that are not linearly related, and inverse proportionality is one such example. In certain probabilistic scenarios, the probability of one event occurring might decrease as a related event increases, creating an inverse relationship. Understanding the principles outlined in the article Axioms of Probability: Understanding the Principles is crucial for comprehending the mathematical foundations of probability and applying them to situations involving inverse proportionality.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does inversely proportional mean?
Inversely proportional refers to a relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable results in a decrease in the other variable, or vice versa. This is also known as an inverse variation or reciprocal relation. It is a fundamental concept in physics principles and mathematical models.
2. How is the term ‘inversely proportional’ used in physics principles?
In physics, the term ‘inversely proportional‘ is used to describe relationships where the product of two variables is a constant. An example is the principle that pressure is inversely proportional to volume in a gas (Boyle’s Law). This means that if the volume of a gas increases, the pressure decreases, provided the temperature remains constant.
3. Can you provide an example of an inversely proportional relationship?
A common example of an inversely proportional relationship is the speed at which a car travels and the time it takes to reach a destination. If you increase your speed (assuming a constant distance), the time it will take to reach your destination decreases. This is an application of the concept of inverse proportionality.
4. How is the concept of inversely proportional used in mathematical models?
In mathematical models, the concept of inversely proportional is often used to describe a negative correlation between two dependent variables. For instance, in the equation y = k/x, y is inversely proportional to x, where k is the constant of variation or proportionality constant.
5. What is the proportionality constant in an inversely proportional relationship?
In an inversely proportional relationship, the proportionality constant, often denoted by k, is the constant value obtained when the product of the variables is calculated. It is a key part of the algebraic expression representing the relationship.
6. What is the difference between directly proportional and inversely proportional?
When two variables are directly proportional, an increase in one results in a proportional increase in the other. However, when two variables are inversely proportional, an increase in one results in a proportional decrease in the other. These principles are fundamental in understanding linear relationships and inverse functions in mathematics and physics.
7. How does the concept of inversely proportional relate to ratio and proportion?
In the concept of ratio and proportion, ‘inversely proportional‘ means that the ratio of two variables is constant. This is also known as a constant ratio or inverse ratio. When one variable increases, the other decreases at a rate that maintains this constant ratio.
8. What is an inverse proportionality in terms of scientific laws?
Inverse proportionality in scientific laws refers to situations where one quantity is inversely proportional to another. For example, according to Coulomb’s Law, the force between two charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
9. How is the concept of inversely proportional used in quantitative analysis?
In quantitative analysis, the concept of inversely proportional is used to understand and predict how changes in one variable will affect another. This is particularly useful when modeling complex systems or phenomena where variables have a reciprocal relation.
10. What does the term ‘inverse proportion’ mean?
‘Inverse proportion‘ is another term for ‘inversely proportional‘. It describes a relationship between two variables where an increase in one variable results in a decrease in the other, or vice versa, at a constant rate. This is represented by the equation y = k/x, where k is the constant of proportionality.
Also Read:
- Osmosis vs diffusion
- Volume of a cylinder
- Axiom and postulate
- What is a heading indicator directional gyro
- Vapour condensation
- Overdamped vs critically damped
- Is cytosine a pyrimidine
- Actuators
- Autorefractor
- Adsorption isotherm

The TechieScience Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the TechieScience.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.
